About Targa Resources
Targa Resources Corp. (Targa) operates as a provider of midstream services. The company is an independent midstream infrastructure company in North America. The company owns, operates, acquires, and develops a diversified portfolio of complementary domestic midstream infrastructure assets.

The company engages primarily in the business of gathering, compressing, treating, processing, transporting, and purchasing and selling natural gas; transporting, storing, fractionating, treating, and purchasing and selling NGLs and natural gas liquid (NGL) products, including services to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) exporters; and gathering, storing, terminaling, and purchasing and selling crude oil.
The company provides a comprehensive package of services to natural gas and crude oil producers. These services are essential to gather, process, treat, purchase and sell and transport wellhead gas to meet pipeline standards; extract, transport and fractionate NGLs for sale into petrochemical, industrial, commercial and export markets; and gather and/or purchase and sell crude oil. The company’s transportation assets further enhance its integrated midstream service offerings across the NGL and natural gas value chain by linking supply to key markets. The company’s gathering and processing infrastructure is located in attractive oil and gas producing basins and is well positioned within each of those basins. The company’s fractionation assets are primarily located in key NGL market centers and are near and connected to key consumers of NGL products, including the petrochemical and industrial markets. The company’s logistics assets, including fractionation facilities, storage wells, its low ethane propane de-ethanizer, and its Galena Park Marine Terminal and related pipeline systems and interconnects, include connections to a number of mixed NGL (mixed NGLs or Y-grade) supply pipelines, storage, interconnection and takeaway pipelines and other transportation infrastructure. The company’s gathering and processing systems and logistics and transportation assets consist of high-quality, well-maintained facilities, resulting in low-cost, efficient operations. Advanced technologies have been implemented for processing plants (primarily cryogenic units utilizing centralized control systems), measurement systems (essentially all electronic and electronically linked to a central data-base) and operations and maintenance management systems to manage work orders and implement preventative maintenance schedules (computerized maintenance management systems). The company provides its services under predominantly fee-based contract terms to a diverse mix of customers across its areas of operation.
Segments
The company operates in two primary segments, Gathering and Processing; and Logistics and Transportation (also referred to as the Downstream Business).
Gathering and Processing segment includes assets used in the gathering and/or purchase and sale of natural gas produced from oil and gas wells, removing impurities and processing this raw natural gas into merchantable natural gas by extracting NGLs; and assets used for the gathering and terminaling and/or purchase and sale of crude oil. The Gathering and Processing segment’s assets are located in the Permian Basin of West Texas and Southeast New Mexico (including the Midland, Central and Delaware Basins); the Eagle Ford Shale in South Texas; the Barnett Shale in North Texas; the Anadarko, Ardmore, and Arkoma Basins in Oklahoma (including the SCOOP and STACK) and South Central Kansas; the Williston Basin in North Dakota (including the Bakken and Three Forks plays); and the onshore and near offshore regions of the Louisiana Gulf Coast and the Gulf of Mexico.

Logistics and Transportation segment includes the activities and assets necessary to convert mixed NGLs into NGL products and also includes other assets and value-added services, such as transporting, storing, fractionating, terminaling, and marketing of NGLs and NGL products, including services to LPG exporters and certain natural gas supply and marketing activities in support of the company’s other businesses. The Logistics and Transportation segment also includes the Grand Prix NGL Pipeline (Grand Prix), which connects the company’s gathering and processing positions in the Permian Basin, Southern Oklahoma and North Texas with its Downstream facilities in Mont Belvieu, Texas. The company’s Downstream facilities are located predominantly in Mont Belvieu and Galena Park, Texas, and in Lake Charles, Louisiana.
Business Operations
The company’s operations are reported in two segments, Gathering and Processing; and Logistics and Transportation (also referred to as the Downstream Business).
Gathering and Processing segment
The company’s Gathering and Processing segment consists of gathering, compressing, treating, processing, transporting, and purchasing and selling natural gas and gathering, storing, terminaling and purchasing and selling crude oil. The gathering or purchase of natural gas consists of aggregating natural gas produced from various wells through varying diameter gathering lines to processing plants. Natural gas has a widely varying composition depending on the field, the formation and the reservoir from which it is produced. The processing of natural gas consists of the extraction of embedded NGLs and the removal of water vapor and other contaminants to form a stream of marketable natural gas, commonly referred to as residue gas, and a stream of mixed NGLs. Once processed, the residue gas is transported to markets through residue gas pipelines. End-users of residue gas include large commercial and industrial customers, as well as natural gas and electric utilities serving individual consumers. The company sells its residue gas either directly to such end-users or to marketers into intrastate or interstate pipelines, which are typically located in close proximity or with ready access to its facilities. The gathering or purchase of crude oil consists of aggregating crude oil production through the company’s pipeline gathering systems, which deliver crude oil to a combination of other pipelines, rail and truck.
The company continually seeks new supplies of natural gas and crude oil, both to offset the natural decline in production from connected wells and to increase throughput volumes. The company obtains additional natural gas and crude oil supply in its operating areas by contracting for production from new wells or by capturing existing production gathered by others. Competition for new natural gas and crude oil supplies is based primarily on location of assets, commercial terms including pre-existing contracts, service levels and access to markets.
The Gathering and Processing segment’s assets are located in the Permian Basin of West Texas and Southeast New Mexico (including the Midland, Central and Delaware Basins); the Eagle Ford Shale in South Texas; the Barnett Shale in North Texas; the Anadarko, Ardmore, and Arkoma Basins in Oklahoma (including the SCOOP and STACK) and South Central Kansas; the Williston Basin in North Dakota (including the Bakken and Three Forks plays) and in the onshore and near offshore regions of the Louisiana Gulf Coast and the Gulf of Mexico. The natural gas processed in this segment is supplied through its gathering systems which, in aggregate, consist of approximately 31,000 miles of natural gas pipelines and include 52 owned and operated processing plants.
The Gathering and Processing segment’s operations consist of Permian Midland and Permian Delaware (also referred to as Permian), SouthTX, North Texas, SouthOK, WestOK (also referred to as Central), Coastal and Badlands.
Permian Midland
The Permian Midland system consists of approximately 7,400 miles of natural gas gathering pipelines and 19 processing plants with an aggregate processing capacity of 3,589 MMcf/d, all located within the Permian Basin in West Texas. Eleven of these plants and approximately 5,200 miles of gathering pipelines belong to a joint venture (WestTX), in which the company has an approximate 72.8% ownership. Pioneer Natural Resources (Pioneer), a major producer in the Permian Basin, owns the remaining interest in the WestTX system.
In response to increasing production and to meet the infrastructure needs of producers, the company is constructing the Greenwood II plant, a new 275 Million cubic feet per day (MMcf/d) cryogenic natural gas plant, which is expected to begin operations in the fourth quarter of 2024.
Permian Delaware
The Permian Delaware system consists of approximately 7,200 miles of natural gas gathering pipelines and 16 processing plants with an aggregate capacity of 3,055 MMcf/d, within the Delaware Basin and Central Basin in West Texas and Southeastern New Mexico.
In response to increasing production and to meet the infrastructure needs of producers, the company is constructing the Bull Moose plant, a new 275 MMcf/d cryogenic natural gas processing plant, which is expected to begin operations in the second quarter of 2025. Additionally, the company is transferring an existing cryogenic natural gas processing plant to Permian Delaware, which will be installed as a new 230 MMcf/d Roadrunner II plant, and is expected to begin operations in the second quarter of 2024.
SouthTX
The South Texas system contains approximately 2,100 miles of high-pressure and low-pressure gathering and transmission pipelines and three natural gas processing plants in the Eagle Ford Shale with an aggregate processing capacity of 660 MMcf/d. The South Texas system processes natural gas through the Silver Oak I, Silver Oak II and Raptor gas processing plants.
For most of 2023, the company owned a 50% interest in Carnero G&P LLC (Carnero). Carnero owns and Targa operates the Silver Oak II plant, the Raptor plant and approximately 50 miles of high-pressure gathering pipeline located in La Salle, Dimmitt and Webb Counties, Texas which connects Mesquite Energy Inc.’s Catarina Ranch gathering system and Comanche Ranch acreage to the Raptor plant. In December 2023, the company completed the acquisition of the remaining 50% membership interest in Carnero G&P LLC (Carnero) from the company’s joint venture partner.
North Texas
North Texas includes the Chico gathering system in the Fort Worth Basin, which gathers gas from the Barnett Shale and Marble Falls plays for processing at the Chico plant with a processing capacity of 265 MMcf/d. The system consists of approximately 4,700 miles of pipelines gathering wellhead natural gas.
SouthOK
The SouthOK gathering system is located in the Ardmore and Anadarko Basins and includes the Golden Trend, SCOOP, and Woodford Shale areas of southern Oklahoma. The gathering system consists of approximately 1,600 miles of pipelines in 12 counties.
The SouthOK system includes five separate processing plants with an aggregate processing capacity of 630 MMcf/d, including: the Stonewall, Hickory Hills and Tupelo facilities, which are owned by the company’s Centrahoma Joint Venture, and its wholly-owned Velma and Velma V-60 plants. The company has a 60% ownership interest in Centrahoma. The remaining 40% ownership interest in Centrahoma is held by MPLX, LP.
WestOK
The WestOK gathering system is located in north central Oklahoma and southern Kansas’ Anadarko Basin and includes the Woodford shale and the STACK. The gathering system consists of approximately 6,600 miles of pipelines in 14 counties.
The WestOK system has an aggregate processing capacity of 400 MMcf/d with two separate cryogenic natural gas processing plants known as the Waynoka I and Waynoka II facilities.
Coastal
The company’s Coastal assets, located in and offshore Louisiana, gather and process natural gas produced from shallow-water central and western Gulf of Mexico natural gas wells and from deep shelf and deep-water Gulf of Mexico production via connections to third-party pipelines or through pipelines owned by it. The Coastal system has an aggregate processing capacity of 2,025 MMcf/d and 11 MBbl/d of integrated fractionation capacity, and consists of approximately 1,000 miles of onshore gathering system pipelines, and approximately 100 miles of offshore gathering system pipelines. The processing plants are comprised of three wholly-owned and operated plants, one partially owned and operated plant, and one partially owned, non-operated plant. The company’s Coastal plants have access to markets across the U.S. through the interstate natural gas pipelines to which they are interconnected. The industry continues to rationalize gas processing capacity along the western Louisiana Gulf Coast with most of the producer volumes going to more efficient plants, such as its Lowry and Gillis plants.
Badlands
The company’s Badlands operations are located in the Bakken and Three Forks Shale plays of the Williston Basin in North Dakota and include approximately 500 miles of crude oil gathering pipelines, 120 Thousand barrels (MBbl) of operational crude oil storage capacity at the Johnsons Corner Terminal, 30 MBbl of operational crude oil storage capacity at the Alexander Terminal, 30 MBbl of operational crude oil storage at New Town and 25 MBbl of operational crude oil storage at Stanley. The Badlands assets also include approximately 300 miles of natural gas gathering pipelines and the Little Missouri I-III natural gas processing plants, which have a processing capacity of 90 MMcf/d. Additionally, Targa operates the 200 MMcf/d Little Missouri 4 plant (LM4 plant), in which Targa Badlands and Hess Midstream Partners LP each own a 50% interest. Targa owns 55% of Targa Badlands through a joint venture with Blackstone Credit and Blackstone Tactical Opportunities (collectively, Blackstone). The joint venture is a consolidated subsidiary and its financial results and related statistics are presented on a gross basis. Targa Badlands pays a minimum quarterly distribution (MQD) to Blackstone and Targa, with Blackstone having a priority right to the MQDs. Additionally, Blackstone’s capital contributions have a liquidation preference upon a sale of Targa Badlands. Targa Badlands is a discrete entity and the assets and credit of Targa Badlands are not available to satisfy the debts and other obligations of Targa or its other subsidiaries.
Logistics and Transportation segment
The company’s Logistics and Transportation segment is also referred to as its Downstream Business. The company’s Downstream Business includes the activities and assets necessary to transport and convert mixed NGLs into NGL products and also includes other assets and value-added services. The Logistics and Transportation segment includes Grand Prix and associated assets, which are generally connected to and supplied in part by its Gathering and Processing segment. These assets are located predominantly in Mont Belvieu and Galena Park, Texas, and in Lake Charles, Louisiana. The company’s fractionation, pipeline transportation, storage and terminaling businesses include approximately 2,300 miles of company-owned pipelines to transport mixed NGLs and specification products.
The Logistics and Transportation segment also transports, distributes, purchases and sells and markets NGLs via terminals and transportation assets across the U.S. The company owns or markets products at terminal facilities in a number of states, including Alabama, Arizona, California, Florida, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, New Jersey, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Texas and Washington. The geographic diversity of the company’s assets provides direct access to many NGL customers, as well as markets via trucks, barges, ships, rail cars and open-access regulated NGL pipelines owned by third parties.
Transportation Pipelines
The company’s primary pipeline asset is Grand Prix, which connects its gathering and processing positions throughout the Permian Basin, North Texas, and Southern Oklahoma (as well as third-party positions) to its fractionation and storage complex in the NGL market hub at Mont Belvieu, Texas. Grand Prix transports NGLs from the Permian Basin on a 24-inch diameter pipeline, which can transport 600 MBbl/d, and from North Texas and South and Central Oklahoma via a pipeline of varying capacity, which both connect to a 30-inch diameter segment into Mont Belvieu, which is expandable to 1,000 MBbl/d. In January 2023, the company announced and closed on the Grand Prix Transaction. Following the closing of the Grand Prix Transaction, it owns 100% of Grand Prix.
The company is constructing the Daytona NGL Pipeline as an addition to Grand Prix. The pipeline will transport NGLs from the Permian Basin and connect to the 30-inch diameter segment of Grand Prix in North Texas, where volumes will be transported to the company’s fractionation and storage complex in the NGL market hub at Mont Belvieu, Texas. The Daytona NGL Pipeline is expected to be in service in the fourth quarter of 2024.
Through its 50% ownership interest in Cayenne Pipeline, LLC (Cayenne), the company operates the Cayenne pipeline, which transports mixed NGLs from VESCO in Venice, Louisiana, to an interconnection with a third-party NGL pipeline in Toca, Louisiana.
Fractionation
After being extracted in the field, mixed NGLs are typically transported to a centralized facility for fractionation where the mixed NGLs are separated into discrete NGL products: ethane, ethane-propane mix, propane, normal butane, iso-butane and natural gasoline. Sufficient volumes of mixed NGLs will be available for fractionation in commercially viable quantities for the foreseeable future due to historical increases in NGL production from shale plays and other shale-technology-driven resource plays in areas of the U.S. that include Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma and the Rockies and certain other basins accessed by pipelines to Mont Belvieu, as well as from conventional production of NGLs in areas such as the Permian Basin, Mid-Continent, East Texas, South Louisiana and shelf and deep-water Gulf of Mexico.
At its Mont Belvieu operated facility, the company has eight fractionation trains, representing an aggregate capacity of 843.0 MBbl/d, including five fractionation trains with an aggregate capacity of 493.0 MBbl/d that are part of its 88%-owned Cedar Bayou Fractionators; Train 6, a 110 MBbl/d fractionation train, which is wholly-owned by Targa; Train 7, a 120 MBbl/d fractionation train, a joint venture between Targa and the Williams Companies, Inc., in which Targa owns an 80% equity interest; and Train 8, a 120 MBbl/d fractionation train, which is wholly-owned by Targa. Certain fractionation-related infrastructure for Train 7, such as storage caverns and brine handling, were funded and are owned 100% by Targa. The company’s fractionation trains are fully integrated with its existing Gulf Coast NGL storage, terminaling and delivery infrastructure, which includes an extensive network of connections to key petrochemical and industrial customers as well as its LPG export terminal at Galena Park on the Houston Ship Channel.
The company is also constructing Train 9 and Train 10, each 120 MBbl/d fractionation trains, at its Mont Belvieu operated facility, which are expected to begin operations in the second quarter of 2024 and the first quarter of 2025, respectively.
The company additionally has a wholly-owned and operated fractionation facility in Lake Charles, Louisiana, representing a capacity of 55.0 MBbl/d.
In addition to its operated facilities, the company holds an equity investment in GCF, also located at Mont Belvieu. In January 2021, the GCF facility was temporarily idled. The company assumed operatorship of GCF in the first half of 2021. In January 2023, the company reached an agreement with its partners to reactivate the GCF facility. The facility is expected to be operational in the second quarter of 2024.
The company also owns fractionation assets in Monument, New Mexico, and Gillis, Louisiana, which are included in its Gathering and Processing segment. In addition, the company has a natural gasoline hydrotreater at Mont Belvieu, Texas, with a capacity of 35.0 MBbl/d that removes sulfur from natural gasoline, allowing customers to meet stringent fuel content standards.
NGL Storage and Terminaling
In general, the company’s NGL storage assets provide warehousing of mixed NGLs, NGL products and petrochemical products in underground wells, which allows for the injection and withdrawal of such products at various times in order to meet supply and demand cycles. Similarly, the company’s terminaling operations provide the inbound/outbound logistics and warehousing of mixed NGLs, NGL products and petrochemical products in above-ground storage tanks. The company’s NGL underground storage and terminaling facilities serve single markets, such as propane, as well as multiple products and markets. For example, the Mont Belvieu and Galena Park facilities have extensive pipeline connections for mixed NGL supply and delivery of component NGLs, including Grand Prix. In addition, some of its facilities are connected to marine, rail and truck loading and unloading facilities that provide services and products to its customers. The company provides long and short-term storage and terminaling services and throughput capability to third-party customers for a fee.
Across the Logistics and Transportation segment, the company owns 34 storage wells at its facilities with a gross NGL storage capacity of approximately 77 MMBbl and operate seven non-owned wells. The usage of these wells may be limited by brine handling capacity, which is utilized to displace NGLs from storage.
The company operates its storage and terminaling facilities to support its key fractionation facilities at Mont Belvieu and Lake Charles for receipt of mixed NGLs and storage of fractionated NGLs to service the petrochemical, refinery, export and heating customers/markets, as well as its wholesale domestic terminals that focus on logistics to service the heating market customer base. The company’s international export assets include its facilities at both Mont Belvieu and the Galena Park Marine Terminal near Houston, Texas, which have the capability to load propane, butanes and international grade low ethane propane. The export facilities have an effective export capacity of approximately 13.5 MMBbl per month, subject to a mix of propane and butane demand, vessel size and availability of supply, and a variety of other factors. The company has the capability to load VLGC vessels, alongside small and medium sized export vessels. The company continues to experience demand growth for U.S.-based NGLs (both propane and butane) for export into international markets.
NGL Distribution and Marketing
The company markets its own NGL production and also purchase component NGL products from other NGL producers and marketers for resale. The company also purchases product for resale in its Logistics and Transportation segment.
The company generally purchases mixed NGLs at a monthly pricing index less applicable fractionation, transportation and marketing fees and resell these component products to petrochemical manufacturers, refiners and other marketing and retail companies.
Wholesale Domestic Marketing
The company’s wholesale domestic propane marketing operations primarily sell propane and related logistics services to major multi-state retailers, independent retailers and other end-users. The company’s propane supply originates from both its refinery/gas supply contracts and its other owned or managed Logistics and Transportation assets. The company sells propane at a fixed posted price or at a market index basis at the time of delivery and in some circumstances, it earns margins on a netback basis.
The wholesale domestic propane marketing business is significantly impacted by seasonal and weather-driven demand, particularly in the winter, which can impact the price and volume of propane sold in the markets the company serves.
Refinery Services
In its refinery services business, the company typically provides NGL balancing services through contractual arrangements with refiners in several locations to purchase and/or market propane and to supply butanes. The company uses its commercial transportation assets and contract for and use the storage, transportation and distribution assets included in its Logistics and Transportation segment to assist refinery customers in managing their NGL product demand and production schedules. This includes both feedstocks consumed in refinery processes and the excess NGLs produced by other refining processes. Under typical netback purchase contracts, the company retains a portion of the resale price of NGL sales or receive a fixed minimum fee per gallon on products sold. Key factors impacting the results of the company’s refinery services business include production volumes, prices of propane and butanes, as well as its ability to perform receipt, delivery and transportation services in order to meet refinery demand.
Commercial Transportation
The company’s NGL transportation and distribution infrastructure includes a wide range of assets supporting both third-party customers and the delivery requirements of its marketing and asset management business. The company provides fee-based transportation services to refineries and petrochemical companies throughout the Gulf Coast area. The company’s assets are also deployed to serve its wholesale domestic distribution terminals, fractionation facilities, underground storage facilities and pipeline injection terminals. These distribution assets provide a variety of ways to transport products to and from the company’s customers. As of December 31, 2023, the company leased and managed 605 railcars and 137 tractors, and owned 12 tractors, six vacuum trucks, and two pressurized NGL barges.
Natural Gas Marketing
The company also markets natural gas available to it from the Gathering and Processing segment, purchase and resell natural gas in selected U.S. markets and manage the scheduling and logistics for these activities.
Seasonality
Parts of the company’s business are impacted by seasonality.
Acquisitions
In January 2023, the company completed the acquisition of Blackstone Energy Partners’ 25% interest in the entity that owns the Permian to Mont Belvieu segment of Grand Prix (the Grand Prix Transaction). Following the closing of the Grand Prix Transaction, the company owns 100% of Grand Prix, including the Daytona NGL Pipeline.
Regulation of Operations
The company’s intrastate pipelines located in Texas are regulated by the Railroad Commission of Texas (the ‘RRC’) and may be required to have tariffs on file with the RRC. Some of these Texas intrastate pipelines also transport natural gas in interstate commerce pursuant to Section 311 of the Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978 (NGPA). Under Sections 311 and 601 of the NGPA, an intrastate pipeline may transport natural gas in interstate commerce without becoming subject to Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) regulation as a ‘natural-gas company’ under the NGA, but must file the terms and conditions of transportation of natural gas under authority of Section 311 with FERC, and these terms and conditions must be ‘fair and equitable.’ Specifically, during 2023, TPL SouthTex Transmission Company LP, Targa Midland Gas Pipeline LLC, Midland-Permian Pipeline LLC, Delaware-Permian Pipeline LLC, Targa SouthTex Mustang Transmission Ltd., and Targa SouthTex Transmission LP provided NGPA Section 311 service. On August 31, 2023, TPL SouthTex Transmission Company LP and Targa SouthTex Transmission LP merged, with TPL SouthTex Transmission Company LP being the surviving entity. Accordingly, Targa SouthTex Transmission LP filed to cancel its Statement of Operating Conditions for Section 311 transportation service with FERC on September 28, 2023.
The company’s Louisiana intrastate pipeline, Targa Louisiana Intrastate LLC, and the rates and terms of service on the pipeline are subject to regulation by the Office of Conservation of the Louisiana Department of Natural Resources (DNR).
Various federal agencies within the U.S. Department of the Interior, particularly the federal Bureau of Land Management (BLM), Office of Natural Resources Revenue and the Bureau of Indian Affairs, along with the Three Affiliated Tribes, promulgate and enforce regulations pertaining to operations on the Fort Berthold Indian Reservation, on which the company operates a significant portion of its Badlands gathering and processing assets. The Three Affiliated Tribes is a sovereign nation having the right to enforce certain laws and regulations independent from federal, state and local statutes and regulations.
Many of the company’s natural gas, NGL and crude oil pipelines are subject to regulation by the federal Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA), an agency of the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT), under the Natural Gas Pipeline Safety Act of 1968, as amended (NGPSA), with respect to natural gas, and the Hazardous Liquids Pipeline Safety Act of 1979, as amended (HLPSA), with respect to crude oil, NGLs and condensates. The company has obtained a certificate of public convenience and necessity from FERC waiving certain of the Commission’s tariff and rate regulations.
History
Targa Resources Corp., a publicly traded Delaware corporation, was founded in 2005. The company was incorporated in 2005.

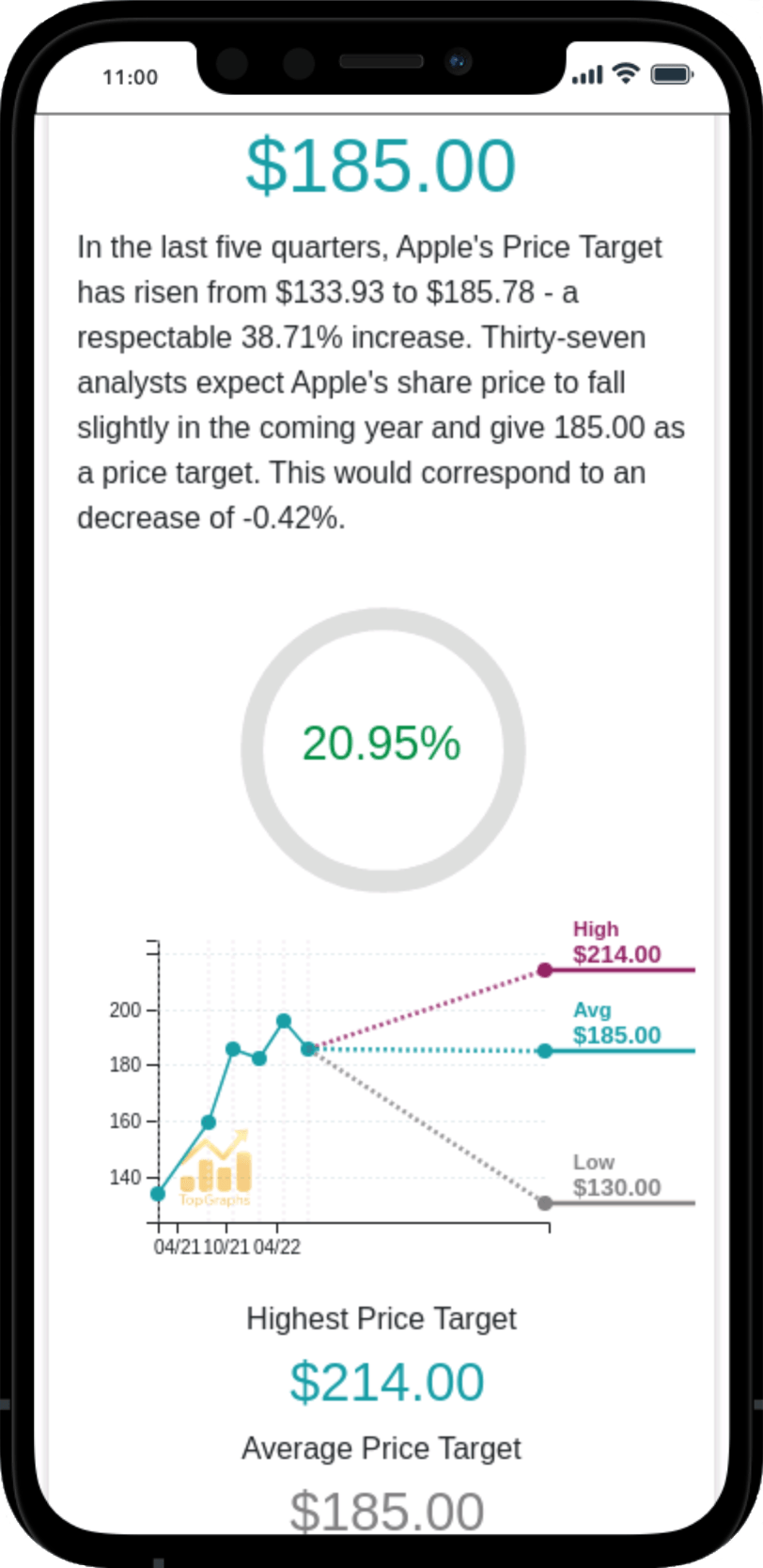
 Stock Value
Stock Value