About Sempra
Sempra operates as a California-based holding company with energy infrastructure investments in North America. The company's businesses invest in, develop and operate energy infrastructure, and provide electric and gas services to customers.
The company has expanded its regulated public utility presence into Texas through the company's 80.25% interest in Oncor and 50% interest in Sharyland Utilities. Sempra Infrastructure's assets include investments in the U.S. and Mexico with a focus on LNG, energy networks and low carbon solutions.
Business Strategy
The company is primarily focused on transmission and distribution investments, among other areas.
Segments
Sempra's business activities are organized under the following reportable segments: Sempra California, Sempra Texas Utilities, and Sempra Infrastructure. SDG&E and SoCalGas each has one reportable segment.

Sempra California
SDG&E
SDG&E is a regulated public utility that provides electric services to a population of, at December 31, 2023, approximately 3.6 million and natural gas services to approximately 3.3 million of that population, covering an approximate 4,100 square mile service territory in Southern California that encompasses San Diego County and an adjacent portion of Orange County.
Electric Transmission and Distribution System
Service to SDG&E's customers is supported by its electric transmission and distribution system, which includes substations and overhead and underground lines. These electric facilities are primarily in the San Diego, Imperial and Orange counties of California, and in Arizona and Nevada and consisted of 1,925 miles of transmission lines, 24,023 miles of distribution lines and 157 substations at December 31, 2023.
SDG&E's 500-kV Southwest Powerlink transmission line, which is shared with Arizona Public Service Company and Imperial Irrigation District, extends from Palo Verde, Arizona to San Diego, California. SDG&E's share of the line is 1,163 MW, although it can be less under certain system conditions. SDG&E's Sunrise Powerlink is a 500-kV transmission line constructed by SDG&E and operated by the California ISO. Both of these lines together provide SDG&E with import capability of 3,900 MW of power.
Mexico's Baja California transmission system is connected to SDG&E's system via two 230-kV interconnections with combined capacity of up to 600 MW in the north-to-south direction and 800 MW in the south-to-north direction. However, it can be less under certain system conditions.
Edison's transmission system is connected to SDG&E's system via five 230-kV transmission lines.
Electric Resources. SDG&E supplies power from its own electric generation facilities and procures power on a long-term basis from other suppliers for resale through CPUC-approved PPAs or purchases on the spot market. SDG&E's electric resources at December 31, 2023 were as follows:
Charges under contracts with suppliers are based on the amount of energy received or are tolls based on available capacity. Tolling contracts are PPAs under which SDG&E provides natural gas to the energy supplier.
SDG&E procures natural gas under short-term contracts for its owned generation facilities and for certain tolling contracts associated with PPAs. Purchases from various southwestern U.S. suppliers are primarily priced based on published monthly bid-week indices, which can be subject to volatility.
SDG&E participates in the Western Systems Power Pool, which includes an electric-power and transmission-rate agreement that allows access to power trading with more than 300 member utilities, power agencies, energy brokers and power marketers throughout the U.S. and Canada. Participants can make power transactions on standardized terms, including market-based rates, preapproved by the FERC. Participation in the Western Systems Power Pool is intended to assist members in managing power delivery and price risk.
Customers and Demand
SDG&E provides electric services through the generation, transmission and distribution of electricity to the following customer classes:
SDG&E provides procurement service for a portion of its customer load. Most customers receive procurement service from a load-serving entity other than SDG&E through programs, such as CCA and DA. In such cases, SDG&E no longer procures energy for this departing load. Accordingly, SDG&E's CCA and DA customers receive primarily transportation and distribution services from SDG&E.
CCA is only available if the customer's local jurisdiction (city or county) offers such a program, as is the case with the City of San Diego and certain other jurisdictions in SDG&E's service territory, and DA is limited by a cap based on gigawatt hours. Several jurisdictions in SDG&E's territory have implemented CCA, including the City of San Diego in 2022. Additional jurisdictions are in the process of implementing or considering CCA.
At December 31, 2023, the residential and commercial rooftop solar capacity in SDG&E's territory totaled 2,154 MW.
SoCalGas
SoCalGas is a regulated public utility that owns and operates a natural gas distribution, transmission and storage system that delivers natural gas to a population of, at December 31, 2023, approximately 21 million, covering an approximate 24,000 square mile service territory that encompasses Southern California and portions of central California (excluding San Diego County, the City of Long Beach and the desert area of San Bernardino County).
Sempra California's Natural Gas Utility Operations
Natural Gas Procurement and Transportation
At December 31, 2023, SoCalGas' natural gas facilities included 3,043 miles of transmission and storage pipelines, 52,404 miles of distribution pipelines, 48,983 miles of service pipelines and nine transmission compressor stations, and SDG&E's natural gas facilities consisted of 197 miles of transmission pipelines, 9,135 miles of distribution pipelines, 6,737 miles of service pipelines and one compressor station.
SoCalGas' and SDG&E's gas transmission pipelines interconnect with four major interstate pipeline systems: El Paso Natural Gas, Transwestern Pipeline, Kern River Pipeline Company, and Mojave Pipeline Company, allowing customers to bring gas supplies into the SoCalGas gas transmission pipeline system from the various out-of-state gas producing basins. Additionally, an interconnection with PG&E's intrastate gas transmission pipeline system allows gas to flow into SoCalGas' gas transmission pipeline system. SoCalGas' gas transmission pipeline system also has an interconnect with a Mexican gas pipeline company at Otay Mesa on the California/Mexico border that allows gas to not only flow south from the gas producing basins in the southwestern U.S., but to also flow north into SoCalGas' gas transmission pipeline system from supplies in Mexico. There are also several in-state gas interconnections allowing for delivery of California-produced gas, including a number of direct connections from renewable natural gas producers.
SoCalGas purchases natural gas under short-term and long-term contracts and on the spot market for SDG&E's and SoCalGas' core customers. SoCalGas purchases natural gas from various sources, including from Canada, the U.S. Rockies and the southwestern regions of the U.S.
To support the delivery of natural gas supplies to its distribution system and to meet the needs of customers, SoCalGas has firm and variable interstate pipeline capacity contracts that require the payment of fixed and variable tariffed and negotiated reservation charges to reserve firm and interruptible transportation rights. Energy companies, primarily El Paso Natural Gas Company, Transwestern Pipeline Company and Kern River Gas Transmission Company, provide transportation services into SoCalGas' intrastate transmission system for supplies purchased by SoCalGas.
Natural Gas Storage
SoCalGas owns four natural gas storage facilities with a combined working gas capacity of 137 Bcf and 128 injection, withdrawal and observation wells that provide natural gas storage service. SoCalGas' and SDG&E's core customers, along with certain third-party market participants, are allocated a portion of SoCalGas' storage capacity. SoCalGas uses the remaining storage capacity for load balancing services for all customers and for storage for noncore customers. Natural gas withdrawn from storage is important to help maintain service reliability during peak demand periods, including consumer heating needs in the winter, as well as peak electric generation needs in the summer. The Aliso Canyon natural gas storage facility has a storage capacity of 86 Bcf and, subject to CPUC limitations, represents 63% of SoCalGas' working natural gas storage capacity. At December 31, 2023, SoCalGas has been authorized by the CPUC to utilize up to 68.6 Bcf of working gas at the facility to help achieve reliability for the region as determined by the CPUC. The authorized storage capacity of the Aliso Canyon natural gas storage facility is subject to an ongoing proceeding with the CPUC.
Customers and Demand
SoCalGas and SDG&E sell, distribute and transport natural gas. SoCalGas purchases and stores natural gas for its core customers in its territory and SDG&E's territory on a combined portfolio basis. SoCalGas also offers natural gas transportation and storage services for others.
End-use customers are classified as either core or noncore customers. Core customers are primarily residential and small commercial and industrial customers.
Most core customers purchase natural gas directly from SoCalGas or SDG&E. While core customers are permitted to purchase their natural gas supplies from producers, marketers or brokers, SoCalGas and SDG&E are obligated to maintain adequate delivery capacity to serve the requirements of all their core customers.
Noncore customers at SoCalGas primarily consist of electric generation, wholesale, and large commercial and industrial customers. A portion of SoCalGas' noncore customers are non-end-users, which include wholesale customers consisting primarily of other utilities, including SDG&E, or municipally owned natural gas distribution systems. Noncore customers at SDG&E consist primarily of electric generation and large commercial customers.
As is prevalent in the industry, subject to regulatory limitations, SoCalGas typically injects natural gas into storage during the months of April through October, and usually withdraws natural gas from storage during the months of November through March.
Sempra Texas Utilities
Sempra Texas Utilities is consisted of the company's equity method investments in Oncor Holdings and Sharyland Holdings. Oncor Holdings is an indirect, wholly owned entity of Sempra that owns an 80.25% interest in Oncor. TTI owns the remaining 19.75% interest in Oncor. Sempra owns an indirect 50% interest in Sharyland Holdings, which owns a 100% interest in Sharyland Utilities.
Oncor
Oncor is a regulated electricity transmission and distribution utility that operates in the north-central, eastern, western and panhandle regions of Texas. Oncor delivers electricity to end-use consumers through its electrical systems, and also provides transmission grid connections to merchant generation facilities and interconnections to other transmission grids in Texas. Oncor's transmission and distribution assets are located in over 120 counties and more than 400 incorporated municipalities, including the cities of Dallas and Fort Worth and surrounding suburbs, as well as Waco, Wichita Falls, Odessa, Midland, Tyler, Temple, Killeen and Round Rock, among others. Most of Oncor's power lines have been constructed over lands of others pursuant to easements or along public highways, streets and rights-of-way pursuant to permits, public utility easements, franchise or other agreements or as otherwise permitted by law.
Because Oncor Holdings and Oncor are managed independently (i.e., ring-fenced), the company accounts for its 100% ownership interest in Oncor Holdings as an equity method investment.
Electricity Transmission
Oncor's electricity transmission business is responsible for the safe and reliable operations of its transmission network and substations. These responsibilities consist of the construction, maintenance and security of transmission facilities and substations and the monitoring, controlling and dispatching of high-voltage electricity over its transmission facilities in coordination with ERCOT.
At December 31, 2023, Oncor's transmission system included approximately 18,298 circuit miles of transmission lines, a total of 1,257 transmission and distribution substations, and interconnection to 173 third-party generation facilities totaling 54,277 MW.
Transmission revenues are provided under tariffs approved by either the PUCT or, to a small degree related to limited interconnection to other markets, the FERC. Network transmission revenues compensate Oncor for delivery of electricity over transmission facilities operating at 60 kV and above. Other services offered by Oncor through its transmission business include system impact studies, facilities studies, transformation service and maintenance of transformer equipment, substations and transmission lines owned by other parties.
Electricity Distribution
Oncor's electricity distribution business is responsible for the overall safe and reliable operation of distribution facilities, including electricity delivery, power quality, security and system reliability. These responsibilities consist of the ownership, management, construction, maintenance and operation of the electricity distribution system within its certificated service area. Oncor's distribution system receives electricity from the transmission system through substations and distributes electricity to end-users and wholesale customers through 3,722 distribution feeders at December 31, 2023.
Oncor's distribution system included nearly 4.0 million points of delivery at December 31, 2023 and consisted of 125,116 circuit miles of overhead and underground lines.
Customers and Demand
Oncor operates the largest transmission and distribution system in Texas based on the number of end-use customers and miles of transmission and distribution lines, delivering electricity to nearly 4.0 million homes and businesses, operating more than 143,000 circuit miles of transmission and distribution lines as of December 31, 2023 in a territory with an estimated population of approximately 13 million. The majority of consumers of the electricity Oncor delivers are free to choose their electricity supplier from retail electric providers who compete for their business. Oncor is not a seller of electricity, nor does it purchase electricity for resale. Rather, Oncor provides wholesale transmission services to its electricity distribution business, as well as non-affiliated electricity distribution companies, electric cooperatives and municipally owned utilities. Oncor also provides distribution services, consisting of retail delivery services to retail electric providers that sell electricity to end-use customers, as well as wholesale delivery services to electric cooperatives and municipally owned utilities. At December 31, 2023, Oncor's distribution business customers primarily consisted of over 100 retail electric providers that sell the electricity it distributes to consumers in its certificated service areas.
Oncor's revenues and results of operations are subject to seasonality, weather conditions and other electricity usage drivers, with revenues being highest in the summer.
Sharyland Utilities
Sharyland Utilities is a regulated electric transmission utility that owns and operates, at December 31, 2023, approximately 64 miles of electric transmission lines in south Texas, including a direct current line connecting Mexico and assets in McAllen, Texas. Sharyland Utilities is responsible for providing safe, reliable and efficient transmission and substation services and investing to support infrastructure needs in its service territory. Transmission revenues are provided under tariffs approved by the PUCT.
Sempra Infrastructure
The company's Sempra Infrastructure segment includes the operating companies of the company's subsidiary, SI Partners, as well as a holding company and certain services companies. SI Partners is included within the company's Sempra Infrastructure reportable segment, but is not the same in its entirety as the reportable segment. Sempra Infrastructure develops, builds, operates and invests in energy infrastructure to help enable the energy transition in North American markets and globally.
At December 31, 2023, Sempra Infrastructure, KKR Pinnacle and ADIA directly or indirectly own a 70%, 20%, and 10% interest, respectively, in SI Partners. SI Partners holds a 100% ownership interest in Sempra LNG Holding, LP and a 99.9% ownership interest in IEnova at December 31, 2023. Sempra Infrastructure consolidates Sempra's ownership and management of its non-U.S. utility, energy infrastructure assets in North America under a single platform. These assets include LNG and natural gas infrastructure in the U.S. and Mexico and renewable energy, LPG and refined products infrastructure in Mexico, which are managed through three business lines: LNG, Energy Networks and Low Carbon Solutions.
LNG
Sempra Infrastructure's LNG business line is consisted of a natural gas liquefaction and regasification portfolio in operation, construction or development, and is focused on securely delivering natural gas to the world in the support of the energy transition.
Cameron LNG Phase 1 Facility
SI Partners owns 50.2% of Cameron LNG JV, while an affiliate of TotalEnergies SE, an affiliate of Mitsui & Co., Ltd., and Japan LNG Investment, LLC (a company jointly owned by Mitsubishi Corporation and Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha) each own 16.6% of Cameron LNG JV. The company accounts for its ownership interest in Cameron LNG JV under the equity method.
Cameron LNG JV owns and operates the Cameron LNG Phase 1 facility, a natural gas liquefaction, export, regasification and import facility with three natural gas pre-treatment, processing and liquefaction trains. The Cameron LNG Phase 1 facility is located in Hackberry, Louisiana, along the Calcasieu Ship Channel, which handles significant industrial shipping, including large oil and LNG tankers, that is well positioned to supply the Atlantic and Pacific markets. The three liquefaction trains have a combined nameplate capacity of 13.9 Mtpa of LNG with an export capacity of 12 Mtpa of LNG, or approximately 1.7 Bcf of natural gas per day. The Cameron LNG Phase 1 facility has 20-year liquefaction and regasification tolling capacity agreements in place with affiliates of TotalEnergies SE, Mitsubishi Corporation and Mitsui & Co., Ltd., which collectively subscribe for the full nameplate capacity of the three trains at the facility.
ECA Regas Facility
Sempra Infrastructure owns and operates the ECA Regas Facility in Baja California, Mexico, which is capable of processing one Bcf of natural gas per day and has a storage capacity of 320,000 cubic meters in two tanks of 160,000 cubic meters each.
The ECA Regas Facility generates revenues from firm storage service fees under firm storage service agreements and nitrogen injection service agreements with Shell Mexico Gas Natural, S. de R.L. de C.V. and SEFE that expire in 2028, which permit them to collectively use 50% of the terminal's capacity, with the remaining 50% of the capacity available for Sempra Infrastructure's use. The land on which the ECA Regas Facility and the ECA LNG liquefaction projects under construction and in development are expected to be situated, as well as land adjacent to those properties, are the subject of litigation.
Sempra Infrastructure uses its 50% capacity at the ECA Regas Facility to satisfy its obligation under an LNG SPA with Tangguh PSC through 2029, and ECA LNG Phase 1 will be the sole user of this capacity thereafter.
ECA LNG Phase 1 Project
SI Partners owns an 83.4% interest in ECA LNG Phase 1, and an affiliate of TotalEnergies SE owns the remaining 16.6% interest. ECA LNG Phase 1 is constructing a one-train natural gas liquefaction facility at the site of Sempra Infrastructure's existing ECA Regas Facility with a nameplate capacity of 3.25 Mtpa and an initial offtake capacity of 2.5 Mtpa. The company expects the ECA LNG Phase 1 project to commence commercial operations in the summer of 2025.
ECA LNG Phase 1 has definitive 20-year SPAs with an affiliate of TotalEnergies SE for approximately 1.7 Mtpa of LNG and Mitsui & Co., Ltd. for approximately 0.8 Mtpa of LNG.
PA LNG Phase 1 Project
SI Partners, KKR Denali and an affiliate of ConocoPhillips directly or indirectly own a 28%, 42% and 30%, respectively, interest in the PA LNG Phase 1 project under construction on a greenfield site in the vicinity of Port Arthur, Texas, located along the Sabine-Neches waterway. The PA LNG Phase 1 project will consist of two liquefaction trains, two LNG storage tanks, a marine berth and associated loading facilities and related infrastructure necessary to provide liquefaction services with a nameplate capacity of approximately 13 Mtpa and an initial offtake capacity of approximately 10.5 Mtpa. The company expects the first and second trains of the PA LNG Phase 1 project to commence commercial operations in 2027 and 2028, respectively.
Sempra Infrastructure has definitive SPAs with an affiliate of ConocoPhillips for a 20-year term for 5 Mtpa of LNG, RWE Supply & Trading GmbH for a 15-year term for 2.25 Mtpa of LNG, INEOS for a 20-year term for approximately 1.4 Mtpa of LNG, ORLEN for a 20-year term for approximately 1 Mtpa of LNG, and ENGIE S.A. for a 15-year term for approximately 0.875 Mtpa of LNG.
Asset and Supply Optimization
Sempra Infrastructure has an LNG SPA through 2029 with Tangguh PSC for the supply of the equivalent of 500 MMcf of natural gas per day at a price based on the SoCal Border index for natural gas. The LNG SPA allows Tangguh PSC to divert certain LNG volumes to other global markets in exchange for payments of diversion fees. Sempra Infrastructure may also enter into short-term supply agreements to purchase LNG to be received, stored and regasified at the ECA Regas Facility for sale to other parties. Sempra Infrastructure uses the natural gas produced from this LNG to supply a contract for the sale of natural gas to the CFE at prices that are based on the SoCal Border index. If LNG volumes received from Tangguh PSC are not sufficient to satisfy the commitment to the CFE, Sempra Infrastructure may purchase natural gas in the market to satisfy such commitment.
Sempra Infrastructure purchases, transports and sells natural gas, and has customers in both the U.S. and Mexico, including the CFE. Sempra Infrastructure may also purchase natural gas from other Sempra affiliates. Natural gas purchases and transportation arrangements are substantially backed by long-term, the U.S. dollar-based contracts for the sale of natural gas to third parties (both the U.S. sourced and derived from imported LNG), LNG offtake and natural gas storage and pipeline capacity.
LNG Projects Under Development. Sempra Infrastructure is evaluating the following development opportunities:
Cameron LNG Phase 2 project, an expansion of the Cameron LNG Phase 1 facility that would add one liquefaction train and debottlenecking capacity from the existing three trains.
ECA LNG Phase 2 project, a large-scale natural gas liquefaction project to be located at the site of Sempra Infrastructure's existing ECA Regas Facility in Baja California, Mexico.
PA LNG Phase 2 project, a large-scale natural gas liquefaction project and associated infrastructure to be located adjacent to the PA LNG Phase 1 project in the vicinity of Port Arthur, Texas.
Vista Pacifico LNG project, a mid-scale natural gas liquefaction project and associated infrastructure in the vicinity of Topolobampo in Sinaloa, Mexico.
Energy Networks
Sempra Infrastructure's Energy Networks business line is consisted of a natural gas transportation and distribution network.
Cross-Border Interconnections and In-Country Pipelines
Sempra Infrastructure develops, builds, operates and invests in systems for the receipt, transportation, compression and delivery of natural gas and ethane. At December 31, 2023, these systems consisted of 1,850 miles of natural gas transmission pipelines plus 136 miles under construction, 16 natural gas compression stations plus one under construction, and 139 miles of ethane pipelines in Mexico. The design capacity of these pipeline assets is over 16,400 MMcf per day of natural gas, 204 MMcf per day of ethane gas and 106,000 barrels per day of ethane liquid. Capacity on Sempra Infrastructure's pipelines and related assets is substantially contracted under long-term, the U.S. dollar-based agreements with major industry participants, such as the CFE, Centro Nacional de Control de Gas, PEMEX, SEFE and other similar counterparties.
Sempra Infrastructure owns a 40-mile natural gas pipeline in south Louisiana, the Cameron Interstate Pipeline, which links the Cameron LNG Phase 1 facility in Cameron Parish in Louisiana to seven pipelines that offer access to major feed gas supply basins in Texas and the northeast, midcontinent and southeast regions of the U.S. The majority of transportation capacity on the Cameron Interstate Pipeline is under long-term transportation service agreements with shippers for delivery to the Cameron LNG Phase 1 facility.
Sempra Infrastructure has made a positive final investment decision on and begun procurement and engineering activities related to the construction of the Port Arthur Pipeline Louisiana Connector, a 72-mile pipeline connecting the PA LNG Phase 1 project to Gillis, Louisiana.
Natural Gas Distribution
Sempra Infrastructure's natural gas distribution regulated utility, Ecogas, operates in three separate distribution zones in Mexicali, Chihuahua and La Laguna-Durango, Mexico. At December 31, 2023, Ecogas had approximately 3,043 miles of distribution pipeline, and approximately 157,000 customer meters serving more than 597,000 residential, commercial and industrial consumers with sales volume of approximately 10 MMcf per day in 2023. Ecogas relies on supply and transportation services from Sempra Infrastructure, SoCalGas and PEMEX for the natural gas it distributes to its customers.
LPG Storage and Associated Systems
Sempra Infrastructure owns and operates the TDF, S. de R. L. de C. V. (TDF) pipeline system and the Guadalajara LPG terminal. At December 31, 2023, the TDF pipeline system consisted of approximately 118 miles of 12-inch diameter LPG pipeline with a design capacity of 34,000 barrels per day and associated storage and dispatch facilities. The TDF pipeline system runs from PEMEX's Burgos facility in the Mexican state of Tamaulipas, Mexico to Sempra Infrastructure's approximately 32,000-barrel LPG storage facility near the city of Monterrey, Mexico and is fully contracted to PEMEX on a firm basis through 2027. Sempra Infrastructure's Guadalajara LPG terminal is an 80,000-barrel LPG storage facility near Guadalajara, Mexico, with associated loading and dispatch facilities, and serves the LPG needs of Guadalajara. The Guadalajara LPG terminal is fully contracted to PEMEX on a firm basis through 2028. Both contracts are U.S. dollar-denominated or referenced and are periodically adjusted for inflation.
Refined Products and Natural Gas Storage
Sempra Infrastructure's refined products storage business develops, constructs and operates systems for the receipt, storage and delivery of refined products, principally gasoline, diesel and jet fuel, throughout the Mexican states of Baja California, Colima, Puebla, Sinaloa, Veracruz and Valle de Mexico for private companies, with a combined storage capacity of 4.6 million barrels fully operating or under construction/commissioning as of December 31, 2023. Construction of the Topolobampo marine terminal was substantially completed in May 2022, at which time commissioning activities commenced. In December 2023, the company received the final pending permit and expect the Topolobampo terminal will commence commercial operations in the second quarter of 2024. The company's customer contracts for its refined products storage business are structured as long-term, the U.S. dollar-denominated, firm capacity storage agreements with counterparties, including Marathon Petroleum Corporation and Valero Energy Corporation. The contracted rate under these contracts is independent from each terminal's regulated rate as determined by the CRE.
Sempra Infrastructure has made a positive final investment decision on and begun procurement and engineering activities related to the construction of Louisiana Storage, a 12.5-Bcf salt dome natural gas storage facility to support the PA LNG Phase 1 project.
Low Carbon Solutions
Sempra Infrastructure's Low Carbon Solutions business line is focused on commercializing and deploying low carbon solutions in the support of meeting the demand for lower carbon and reliable energy supply. The portfolio of resources includes renewable energy infrastructure, a natural gas-fired power plant, as well as hydrogen fuel production and advanced carbon capture, usage and storage technologies that are under development.
Renewable Power Generation
Sempra Infrastructure develops, builds, invests in and operates renewable energy generation facilities that have long-term PPAs to sell the electricity they generate to their customers, which are generally load serving entities, as well as industrial and other customers. Load serving entities sell electric service to their end-users and wholesale customers upon receipt of power delivery from these energy generation facilities, while industrial and other customers consume the electricity to run their facilities. At December 31, 2023, Sempra Infrastructure had a fully contracted, total nameplate capacity of 1,044 MW related to its fully operating wind and solar power generation facilities.
Natural Gas-Fired Generation
Sempra Infrastructure owns and operates the TdM power plant in the vicinity of Mexicali, Baja California, adjacent to the Mexico-U.S. border. TdM is a 625-MW natural gas-fired, combined-cycle power plant that is connected to the company's Gasoducto Rosarito pipeline system, which enables it to receive regasified LNG from the ECA Regas Facility, as well as continental gas supplied from the U.S. on the North Baja pipeline. TdM generates revenue from selling electricity and resource adequacy to the California ISO and to governmental, public utility and wholesale power marketing entities.
Low Carbon Solutions Projects Under Development
Sempra Infrastructure is developing the Cimarrón Wind project, an approximately 300-MW wind generation facility in Baja California, Mexico. In October 2022, Sempra Infrastructure entered into a 20-year PPA, as amended, with Silicon Valley Power for the long-term supply of renewable energy to the City of Santa Clara, California, which is subject to Sempra Infrastructure reaching a final investment decision. Cimarrón Wind would utilize Sempra Infrastructure's existing cross-border high voltage transmission line to interconnect and deliver clean energy to the East County substation in San Diego County. The company expects to make a final investment decision in the first half of 2024.
Sempra Infrastructure is also evaluating the Hackberry Carbon Sequestration development opportunity, which is a carbon capture and sequestration project that is intended to reduce emissions at the Cameron LNG Phase 1 facility and proposed Cameron LNG Phase 2 project.
Regulation
Utility Regulation
California
SDG&E and SoCalGas are principally regulated at the state level by the CPUC, CEC and CARB.
CARB is a department within the California Environmental Protection Agency, an organization that reports directly to the Governor's Office. Sempra Infrastructure is also subject to the rules and regulations of CARB.
The California Geologic Energy Management Division, the CPUC, and various other state and local agencies regulate the operation and maintenance of SoCalGas' natural gas storage facilities.
Texas
Oncor's and Sharyland Utilities' rates are regulated at the state level by the PUCT and, in the case of Oncor, at the city level by certain cities.
The PUCT has adopted rules implementing the state open-access requirements for all utilities that are subject to the PUCT's jurisdiction over electric transmission services, including Oncor.
The U.S. Federal
SDG&E and SoCalGas are also regulated at the federal level by the FERC, the EPA, the DOE and the DOT, and for SDG&E the NRC.
The FERC regulates SDG&E's and SoCalGas' interstate sale and transportation of natural gas. The FERC also regulates SDG&E's transmission and wholesale sales of electricity in interstate commerce, transmission access, rates of return on transmission investment, rates of depreciation, electric rates involving sales for resale and the application of the uniform system of accounts. The U.S. Energy Policy Act governs procedures for requests for electric transmission service. The California IOUs' electric transmission facilities are under the operational control of the California ISO. As member utilities, Oncor and Sharyland Utilities operate within the ERCOT market. To a small degree related to limited interconnections to other markets, Oncor's electric transmission revenues are provided under tariffs approved by the FERC.
The NRC oversees the licensing, construction, operation and decommissioning of nuclear facilities in the U.S., including SONGS, in which SDG&E owns a 20% interest and which was permanently retired in 2013. The NRC and various state regulations require extensive review of these facilities' safety, radiological and environmental aspects.
The DOT, through PHMSA, has established regulations regarding engineering standards and operating procedures, including procedures intended to manage cybersecurity risks, applicable to SDG&E's and SoCalGas' natural gas transmission and distribution pipelines, as well as natural gas storage facilities. The DOT has certified the CPUC to administer oversight and compliance with these regulations for the entities they regulate in California.
ERCOT Market
As member utilities, Oncor and Sharyland Utilities operate within the ERCOT market, which represents approximately 90% of the electricity consumption in Texas. ERCOT is the regional reliability coordinating organization for member electricity systems in Texas and the ISO of the interconnected transmission grid for those systems. ERCOT is subject to oversight by the PUCT and the Texas Legislature.
Oncor and Sharyland Utilities, along with other owners of electric transmission and distribution facilities in Texas, assist the ERCOT ISO in its operations.
Oncor and Sharyland Utilities are subject to reliability standards adopted and enforced by the Texas Reliability Entity, Inc., an independent organization that develops reliability standards for the ERCOT region and monitors and enforces compliance with the standards of the North American Electric Reliability Corporation, including critical infrastructure protection, and ERCOT protocols.
Other U.S. State and Local Territories Regulation
The South Coast Air Quality Management District is the air pollution control agency responsible for regulating stationary sources of air pollution in the South Coast Air Basin in Southern California. The district's territory covers all of Orange County and the urban portions of Los Angeles, San Bernardino and Riverside counties.
Other U.S. Regulation
The FERC regulates certain Sempra Infrastructure assets pursuant to the U.S. Federal Power Act and Natural Gas Act, which provide for FERC jurisdiction over, among other things, sales of wholesale power in interstate commerce, transportation of natural gas in interstate commerce, and siting and permitting of LNG facilities.
Sempra Infrastructure's investment in Cameron LNG JV is subject to regulations of the DOE regarding the export of LNG.
SDG&E, SoCalGas and businesses in which Sempra Infrastructure invests are subject to the DOT rules and regulations regarding pipeline safety. PHMSA, acting through the Office of Pipeline Safety, is responsible for administering the DOT's national regulatory program to help ensure the safe transportation of natural gas, petroleum and other hazardous materials by pipelines, including pipelines associated with natural gas storage, and develops regulations and other approaches to risk management to help ensure safety in design, construction, testing, operation, maintenance and emergency response of pipeline facilities.
SDG&E, SoCalGas and Sempra Infrastructure are also subject to regulation by the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission.
Foreign Regulation
Operations and projects in the company's Sempra Infrastructure segment are subject to regulation by the CRE, ASEA, SENER, the Mexican Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources of Mexico (Secretaría del Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales), and other labor and environmental agencies of city, state and federal governments in Mexico.
Licenses and Permits
The company's utilities in California and Texas obtain numerous permits, authorizations and licenses for, as applicable, the transmission and distribution of natural gas and electricity and the operation and construction of related assets, including electric generation and natural gas storage facilities, some of which may require periodic renewal.
Sempra Infrastructure obtains numerous permits, authorizations and licenses for its electric and natural gas distribution, generation and transmission systems from the local governments where these services are provided. The permits for generation, transportation, storage and distribution operations at Sempra Infrastructure are generally for 30-year terms, with options for renewal under certain regulatory conditions.
Sempra Infrastructure obtains licenses and permits for the construction, operation and expansion of LNG facilities and for the import and export of LNG and natural gas. Sempra Infrastructure also obtains licenses and permits for the construction and operation of facilities for the receipt, storage and delivery of refined products.
Sempra Infrastructure obtains permits, authorizations and licenses for the construction and operation of natural gas storage facilities and pipelines, and in connection with participation in the wholesale electricity market.
History
The company was founded in 1996. It was incorporated in 1996. The company was formerly known as Mineral Energy company and changed its name to Sempra Energy in 1998 and then to Sempra in May 2023.

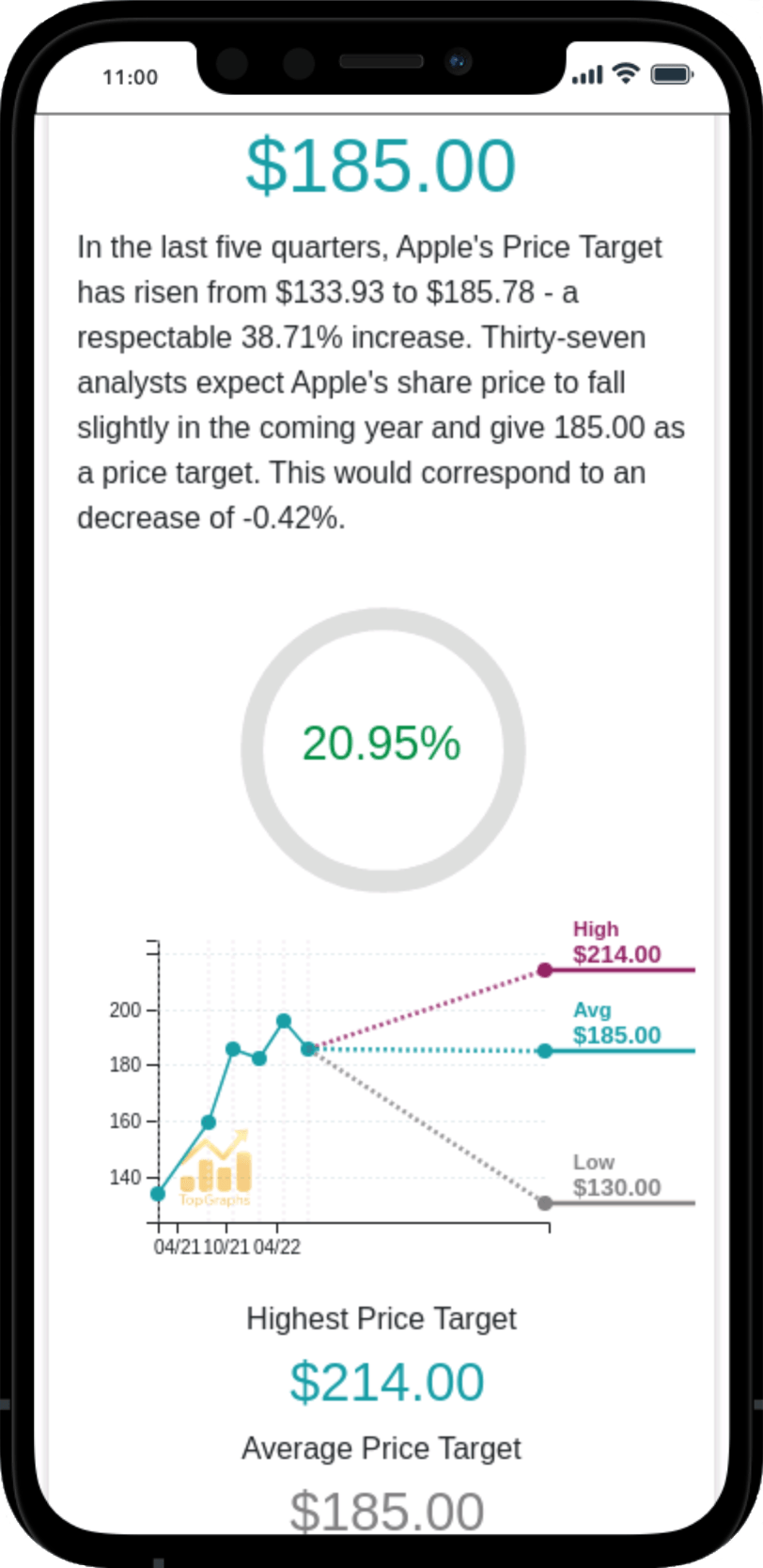
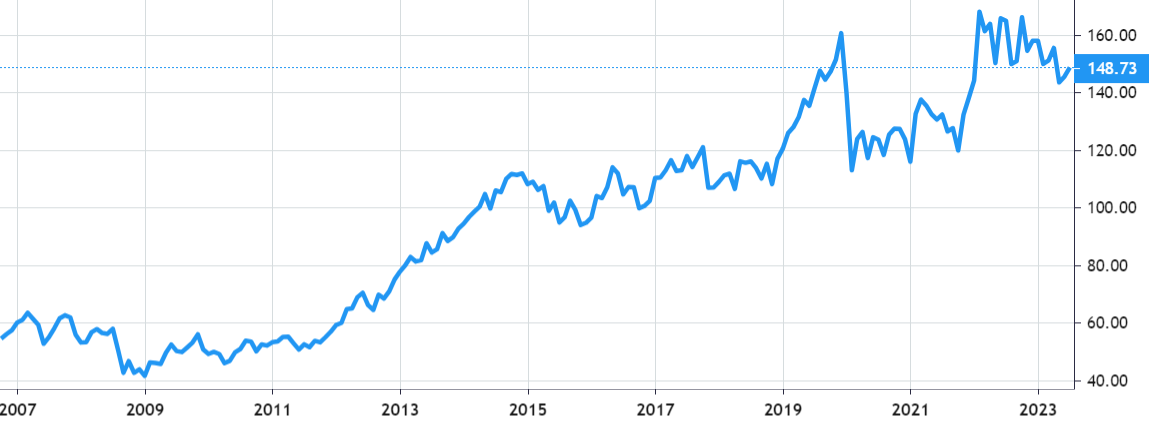
 Stock Value
Stock Value