About Peabody Energy
Peabody Energy Corporation (Peabody) operates as a producer of metallurgical and thermal coal.

As of December 31, 2023, the company owned interests in 17 active coal mining operations located in the United States (U.S.) and Australia, including a 50% equity interest in Middlemount Coal Pty Ltd. (Middlemount). In addition to its mining operations, the company markets and brokers coal from other coal producers; trades coal and freight-related contracts; and since 2022, is partnered in a joint venture with the intent of developing various sites, including certain reclaimed mining land held by the company in the U.S., for utility-scale photovoltaic solar generation and battery storage.
During 2023, Peabody advanced the redevelopment of its North Goonyella Mine in Australia. During the fourth quarter, the mine was renamed to Centurion Mine to reflect the next stage of redevelopment and the company's agreement to acquire an adjacent coal deposit. The first development coal from the Centurion Mine is anticipated in the second quarter of 2024.
Segments
As of December 31, 2023, Peabody reports its results of operations primarily through the following reportable segments: Seaborne Thermal, Seaborne Metallurgical, Powder River Basin, Other U.S. Thermal and Corporate and Other.
Coal Supply Agreements

Customers
Peabody's coal supply agreements are primarily with electricity generators, industrial facilities and steel manufacturers. Most of the company's sales from its mining operations are made under long-term coal supply agreements (those with initial terms of one year or longer and which often include price reopener and/or extension provisions). A smaller portion of the company's sales from its mining operations are made under contracts with terms of less than one year, including sales made on a spot basis.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, Peabody derived 25% of its revenue from coal supply agreements from its five largest customers. Those five customers were supplied primarily from 13 coal supply agreements (excluding trading and brokerage transactions) expiring at various times from 2024 to 2025.
Seaborne Operations
Revenue from Peabody's Seaborne Thermal and Seaborne Metallurgical segments represented approximately 56% of the company's total revenue from coal supply agreements for the year ended December 31, 2023, during which all three periods the coal mining activities of those segments contributed approximately 18% of the company's sales volumes from mining operations.
The U.S. Thermal Operations
Revenue from Peabody's Powder River Basin and Other U.S. Thermal segments, in aggregate, represented approximately 44% of the company's revenue from coal supply agreements for the year ended December 31, 2023, during which all three periods the coal mining activities of those segments contributed approximately 82% of the company's sales volumes from mining operations. The company expects to continue selling a significant portion of coal production from its U.S. thermal operating segments under existing long-term supply agreements.
Transportation
Methods of Distribution
Peabody's U.S. mine sites are typically adjacent to a rail loop; however, in limited circumstances coal may be trucked to a barge site or directly to customers. Title predominately passes to the purchaser at the rail or barge, as applicable. Peabody's U.S. and Australian export coal is usually sold at the loading port, with purchasers paying ocean freight. In each case, the company usually pays transportation costs from the mine to the port, including any demurrage costs (fees paid to third-party shipping companies for loading time that exceeded the stipulated time).
The company has good relationships with U.S. and Australian rail carriers and port and barge companies due, in part, to its modern coal-loading facilities and the experience of its transportation coordinators. Beginning in 2022, rail service constraints due, in part, to labor shortages and weather conditions experienced by Peabody's rail service providers, negatively impacted U.S. thermal shipment volumes. The constraints began to lessen in 2023, resulting in improved rail performance compared to the prior year.
Export Facilities
Peabody has generally secured its ability to transport coal in Australia through rail and port contracts and access to five east coast coal export terminals that are primarily funded through take-or-pay arrangements. In Queensland, seaborne thermal and metallurgical coal from the company's mines is exported through the Dalrymple Bay Coal Terminal, in addition to the Abbot Point Coal Terminal used by its joint venture Middlemount Mine. In New South Wales, the company's primary ports for exporting thermal and metallurgical coal are at Port Kembla and Newcastle, which includes both the Port Waratah Coal Services terminal and the terminal operated by Newcastle Coal Infrastructure Group. Peabody has secured its ability to transport coal from its Shoal Creek Mine under barge and port contracts; the primary port is the McDuffie Terminal in Mobile, Alabama, which the company utilizes without a take-or-pay arrangement.
Peabody's U.S. thermal operations exported less than 1% of their annual tons sold during the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021. No tons were exported during the year ended December 31, 2023. The primary port used for U.S. thermal exports is the Kinder Morgan Terminal near Houston, Texas.
Suppliers
Mining Supplies and Equipment
The principal goods Peabody purchases in the support of its mining activities are mining equipment and replacement parts, diesel fuel, ammonium-nitrate and emulsion-based explosives, off-the-road tires, steel-related products (including roof control materials), lubricants and electricity. Peabody has many well-established, strategic relationships with its key suppliers of goods.
Surface and underground mining equipment demand and lead times for parts and components stabilized throughout 2023. Peabody consistently uses its global leverage with major suppliers and comprehensive planning processes to ensure security of supply to meet the requirements of its active mines.
Services
Peabody also purchases services at its mine sites, including services related to maintenance for mining equipment, construction, temporary labor, use of explosives and various other requirements.
Competition
Peabody's principal U.S. direct coal supply competitors are other large coal producers, including Alliance Resource Partners; American Consolidated Natural Resources, Inc.; Arch Resources, Inc.; CONSOL Energy; Eagle Specialty Materials LLC; Foresight Energy; Hallador Energy; Kiewit; and Navajo Transitional Energy Company LLC, among others.
Environmental Laws and Regulations
In Arizona, where Peabody performs reclamation work on tribal lands, the company is regulated by OSMRE because the tribes do not have SMCRA authorization.
In situations where the company's coal resources are federally owned, the U.S. Bureau of Land Management oversees a substantive exploration and leasing process.
The CAA, enacted in 1970, and comparable state and tribal laws that regulate air emissions affect the company's U.S. coal mining operations both directly and indirectly.
History
Peabody Energy Corporation was founded in 1883. The company was incorporated in Delaware in 1998 and became a public company in 2001.

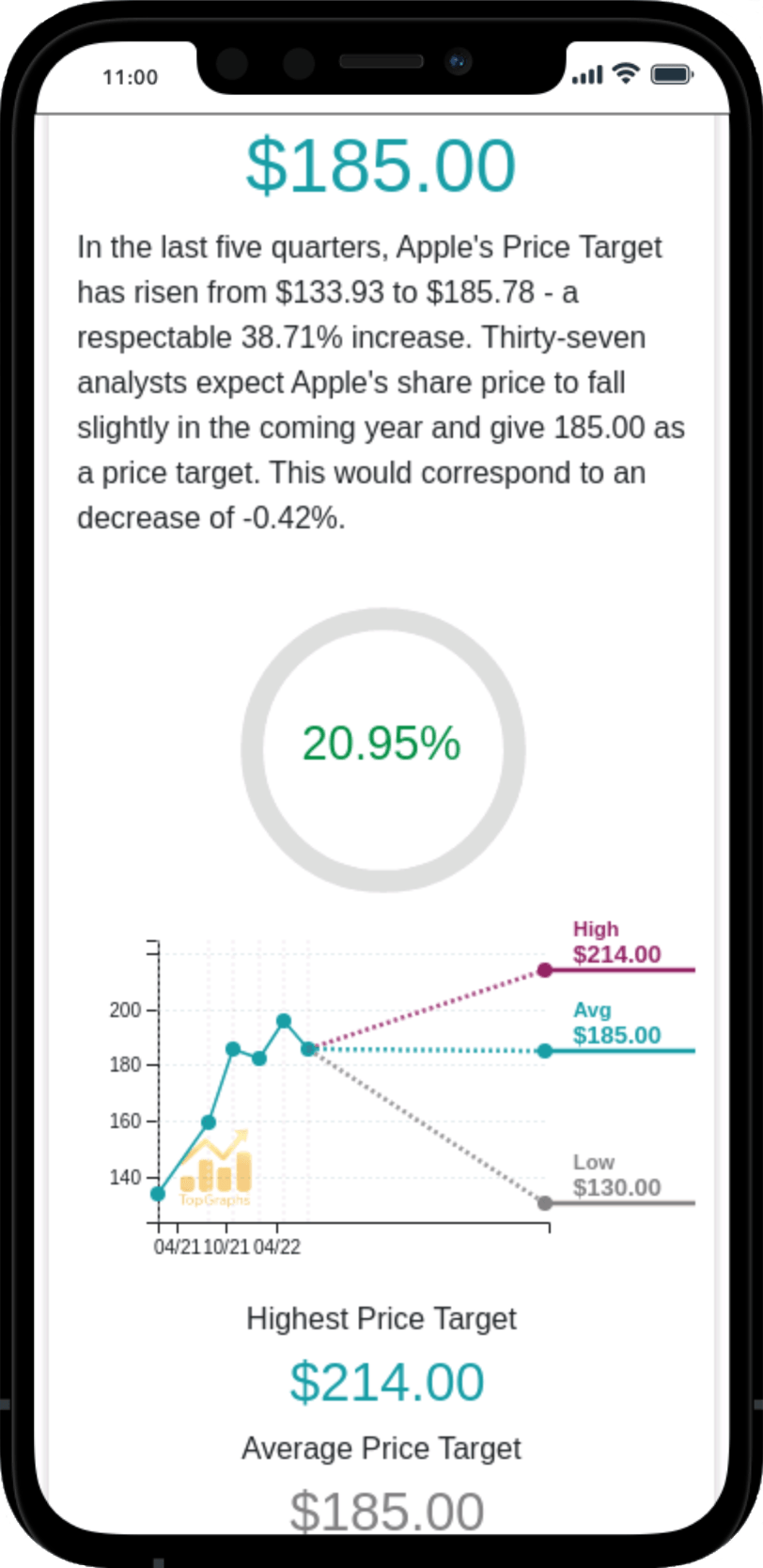
 Stock Value
Stock Value