About Ryanair Holdings
Ryanair Holdings plc (Ryanair Holdings) operates as a scheduled-passenger airline serving short-haul, point-to-point routes mainly within Europe.

As of June 30, 2023, the Ryanair Group had a principal fleet of 530 Boeing 737 aircraft and 28 Airbus A320 aircraft. As of July 21, 2023, the company offered over 3,000 short-haul flights per day serving approximately 230 airports across Europe. The term ‘Ryanair Group’ refers to the wholly owned subsidiary airlines of Ryanair Holdings, including Ryanair Sun S.A. (Buzz), Lauda Europe Limited (Lauda), Malta Air Limited, Ryanair DAC, and Ryanair U.K. Limited.
Route System, Scheduling and Fares
Route System and Scheduling
As of July 21, 2023, the company offered over 3,000 daily scheduled short-haul flights serving approximately 230 airports largely throughout Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.
Ryanair (Ryanair DAC) schedules departures on its most popular routes at frequent intervals normally between approximately 6:00 a.m. and 12:00 a.m.

As part of Ryanair’s AGB customer experience program Ryanair has focused on high frequency and business friendly timings between Europe’s main business centers.
Widely Available Low Fares
Ryanair offers low fares, with prices generally varying on the basis of advance booking, seat availability and demand. Ryanair sells seats on a one-way basis, thus removing minimum stay requirements from all travel on Ryanair scheduled services.
Ryanair also periodically runs special promotional fare campaigns, in particular in connection with the opening of new routes, and endeavors to always offer the lowest fare on any route it serves.
Marketing and Advertising
Ryanair primarily advertises its services in national and regional media across Europe. In addition, Ryanair uses online advertising, email marketing and social media to drive awareness.
Other marketing activities include cooperative advertising campaigns with other travel-related entities, including local tourist boards. Ryanair also regularly contacts people who have registered in its database to inform them about promotions and special offers.
Reservations on Ryanair.com
Passenger airlines generally rely on travel agents (whether traditional or online) for a significant portion of their ticket sales and pay travel agents’ commissions for their services, as well as reimbursing them for the fees charged by reservation systems providers. In contrast, Ryanair requires passengers to make reservations and purchase tickets directly. Due to Ryanair’s long standing online distribution policy, the majority of such reservations and purchases are made through the website Ryanair.com, although a significant number of customers are also booking on the Ryanair app and therefore, the company is not reliant on travel agents.
Ryanair’s reservations system is hosted under an agreement with the system provider, Navitaire. Under the agreement, the system serves as Ryanair’s core seating inventory and booking system. In return for access to these system functions, Ryanair pays transaction fees that are generally based on the number of passenger seat journeys booked through the system. Navitaire also retains back-up booking engines to support operations in the event of a breakdown in the main system.
The company has agreements with the GDS’s Travelport (which operates the Galileo and Worldspan GDS) and Sabre. Since May 2023, Amadeus also has access to Ryanair’s inventory, allowing Ryanair to integrate with corporate booking systems. Ryanair’s fares (except for some promotional fare categories) are distributed on the GDS’s systems but are not available for re-sale on any other online platform, other than Ryanair.com.
Aircraft
Boeing Aircraft
As of June 30, 2023, the company had a fleet of 530 Boeing 737 aircraft, which were operated by Buzz, Malta Air, Ryanair DAC and Ryanair U.K. The fleet includes 119 Boeing 737-8200 aircraft, each having 197 seats, and Boeing 737-800 ‘next generation’ (‘NG’) aircraft, each having 189 seats.
Between March 1999 and March 2023, Ryanair took delivery of 531 new Boeing 737NG aircraft, 1 Boeing 737-700 aircraft and 98 new Boeing 737-8200s under its contracts with Boeing and disposed of 122 Boeing 737NG aircraft, including 77 lease hand-backs. In the period April 2023 to June 2023, Ryanair took delivery of 21 new Boeing 737-8200 aircraft.
Under the terms of the 2014 Boeing Contract, which was repriced in December 2020, Ryanair agreed to purchase 210 new Boeing 737-8200 ‘Gamechanger’ aircraft delivering between fiscal years 2022 and 2025 inclusive. Deliveries commenced in June 2021. The new aircraft will be used on new and existing routes to grow the Ryanair Group’s business.
The Boeing 737-8200 represents the newest generation of Boeing's 737 aircraft. It is a short-to-medium range aircraft and seats 197 passengers (eight (4%) more seats than Ryanair’s existing Boeing 737-800NG 189 seat fleet).
The Boeing 737 is the world’s most widely used commercial aircraft and exists in a number of generations, the Boeing 737-8200 being the most recent in current production.
The Boeing 737NGs are fitted with CFM 56-7B engines and have advanced CAT III Autoland capability, advanced traffic collision avoidance systems, and enhanced ground-proximity warning systems. The Boeing 737-8200s are fitted with CFM LEAP-1B engines, which combined with the Advanced Technology winglet and other aerodynamic improvements, should reduce fuel consumption by up to approximately 16% on a per seat basis compared to the Boeing 737NGs in Ryanair’s configuration and reduce operational noise emissions by approximately 40%.
As of March 31, 2023, the average aircraft age of the company’s Boeing 737 fleet was approximately 9 years.
Airbus Aircraft
As of June 30, 2023, the company had a fleet of 28 leased Airbus A320 aircraft (2022: 29). These aircraft are operated by Lauda, as a wet lease operator for the Group, and have 180 seats. They are powered by a mix of CFM 56-5B and Pratt & Whitney V2500 engines. As of March 31, 2023, the average aircraft age of the company’s leased Airbus A320 fleet was approximately 15.9 years.
The company expects to have an operating fleet comprising approximately 640 narrow-body aircraft as of March 31, 2026, depending on the level of lease hand-backs and aircraft disposals.
In May 2023, Ryanair signed an agreement to purchase 300 new Boeing 737-MAX-10 aircraft (150 firm orders and 150 options), which is subject to shareholder approval at the company’s AGM on September 14, 2023. These fuel-efficient aircraft have 228 seats and phased deliveries between 2027 and 2033. It is expected that up to 50% of the order will be used to replace older Boeing 737NG aircraft, while the remainder will facilitate disciplined traffic growth to approximately 300m passengers per annum by 2034.
Training and Regulatory Compliance
As of March 31, 2023, Ryanair owned and operated 10 Boeing 737-800NG, 6 Boeing 737-8200 and 1 A320 full flight simulators for pilot training. The simulators were purchased from CAE Inc of Quebec, Canada (‘CAE’). In addition, Ryanair owns and operates 9 fixed base simulators from Multi Pilot Simulations (‘MPS’), which are used for pilot assessments and pilot training. In autumn 2021, Ryanair, in partnership with Aviation Flight Academy (‘AFA’), opened a new, state of the art, training center in Dublin which includes both Boeing 737-8200 and A320 full flight simulators, and a full Boeing 737 Cabin Trainer. In the year ended March 31, 2023 (fiscal year 2023), Ryanair took delivery of 3 Boeing 737-8200 full flight simulators and the new fixed based simulator. In 2024, Ryanair will take delivery of 1 Boeing 737-8200 full flight simulator into the Bergamo Training Centre, with no further deliveries planned in 2024. Per the purchase agreement, this leaves a balance of 4 full flight simulators (2 confirmed and 2 options).
Ancillary Services
Ryanair provides various ancillary services and engages in other activities connected with its core air passenger service, including non-flight scheduled services, internet-related services, and the in-flight sale of beverages, food, duty-free and merchandise.
Ryanair primarily markets car hire, travel insurance and accommodation services through its website and mobile app. Ryanair offers car hire services via a contract with RentalCars. Ryanair receives a commission on these sales.
Ryanair markets car parking, fast-track, airport transfers, attractions and activities on its website and mobile app. Ryanair also sells gift vouchers, which are redeemable online.
Maintenance and Repairs
Post Brexit, with the U.K. leaving EASA, aircraft registered in the U.K. are managed in accordance with the U.K. equivalent regulations.
Ryanair Engineering and Safety & Compliance department manage the Continuing Airworthiness of the Group fleet in accordance with Commission Regulation (EU) No. 1321/2014 of 26 November 2014 - Continuing Airworthiness and U.K. Reg. (EU) 1321/2014 - the U.K. Continuing Airworthiness regulation. Each Group Airline holds applicable approval with their respective National Airworthiness Authority (IAA Ireland, TMCAD Malta, Polish CAA and the U.K. CAA), providing robust oversight of all maintenance activities.
Maintenance activities are undertaken in accordance with EASA and U.K. Part 145 as applicable, by Ryanair DAC under IAA approval and approved contracted providers.
Ryanair is approved to deliver maintenance type training courses under EASA and U.K. Part 147 approvals, with 3 approved training sites located across the Ryanair network, in London Stansted, Glasgow Prestwick, and Seville Spain.
Ryanair is itself an EASA Part 145-approved maintenance organization and provides its own routine aircraft maintenance and repair services. Ryanair also performs certain line maintenance checks on its aircraft, including pre-flight and daily checks at some of its bases, as well as A-checks at its Dublin (+4 bays to 6 in 2025), London (Stansted), Madrid (+2 bays to 3 in 2025), Vienna and Bergamo (+2 to 5 bays in 2023) and Malta (+1 bay 2023) facilities to support line maintenance on Boeing 737 and Airbus A320 aircraft. Ryanair also plans to open a new 2 bay hangar in Oporto Portugal in 2025. Ryanair performs the majority of its Boeing 737 heavy airframe maintenance utilizing a Ryanair associated Part 145 approval/organization for heavy maintenance with a seasonal use of third-party maintenance repair and overhaul (the ‘MRO’) facilities. Ryanair operates a 6 bay hangar facility at its base at Glasgow (Prestwick) in Scotland. In addition, Ryanair has hangar facilities in Kaunas, Lithuania (+2 bays to 4 in 2023), Wroclaw, Poland (+2 bays to 4 in 2023), Hahn, Shannon (+3 bays 2023), and Seville (Spain), which are used for C-check maintenance activities. Ryanair plans to grow in Berlin to 3 bays by 2025 and will continue to look for opportunities to invest in additional hangar facilities over the coming years to ensure there is sufficient hangar capacity for the increased fleet size.
Ryanair has a 5 bay hangar and stores facility at its London (Stansted) airport base enabling Ryanair to carry out line maintenance on its expanding fleet. This facility has flight simulators, fixed base simulators and the associated training rooms. Ryanair in partnership with AFA has developed a separate training facility adjacent to the hangar to accommodate a full-size Boeing 737NG training aircraft to allow for cabin crew and engineering training. Ryanair has simulators in its East Midlands facility (both full flight and fixed based). Ryanair operates a 2 bay hangar in Vienna to maintain a mix of Airbus and Boeing aircraft and, in autumn 2021, opened a new pilot and cabin crew training facility in Dublin which accommodates both Boeing and Airbus full flight simulators to meet the increased training needs of the Group. Ryanair has a 30-year sole tenancy agreement with Frankfurt (Hahn) airport where it maintains a 2 bay hangar and stores facility. This facility allows Ryanair to carry out 2-year base maintenance checks. Ryanair has also built a technological center of excellence in Bergamo with full flight simulators, a fixed base simulator and a full-size Boeing 737NG training aircraft to allow for pilot, engineering, and cabin crew training. Ryanair plans to develop further training facilities over the coming years to manage fleet growth.
Maintenance and repair services that may become necessary while an aircraft is located at other airports served by Ryanair are provided by other EASA Part 145-approved contract maintenance providers. Aircraft return each evening to Ryanair’s bases, where they are examined by either Ryanair’s approved personnel or by local EASA Part 145-approved companies.
Heavy Maintenance
Ryanair expects to be dependent on external service contractors for Airbus A320 and Boeing 737 maintenance, particularly for airframe, engine and component maintenance, for the foreseeable future, notwithstanding the capabilities provided by its maintenance facilities.
Ryanair contracts out engine overhaul service for its Boeing 737-800NG aircraft to CFM under a ten-year agreement to December 2027, with an option for extension. This comprehensive maintenance contract provides for the repair and overhaul of the CFM56-7B series engines fitted to Ryanair’s Boeing 737-800NG aircraft, the repair of parts, and general technical support for the fleet of engines. CFM uses its EASA Part 145-approved repair facilities in Cardiff (Wales), Celma (Brazil), Paris (France), Kuala Lumpur (Malaysia), Queretaro (Mexico) and Safran Aero (Morocco). CFM LEAP-1B Engines installed on the Boeing 737-8200 aircraft are subject to warranty by CFM. Any required repairs/overhauls subject to this warranty will be accomplished by CFM at its EASA Part 145-approved repair facilities. Engine maintenance providers are also monitored closely by the national authorities under EASA and national regulations. Ryanair trained engineering staff with both Boeing and CFM in advance of the introduction of the Boeing 737-8200 aircraft to the Ryanair fleet.
Airport Operations
Airport Handling Services
Ryanair provides its own ground services, aircraft handling and passenger services either directly or through self-handling partners at Dublin, Stansted, Spain, Portugal and the majority of the company’s Polish airports. All other airport handling is provided through the airport authorities, either directly through sub-contractors or the airport themselves at airports Ryanair serves. Ground operations work to obtain the most competitive handling rates for ground, aircraft and passenger services across the company’s network by negotiating multiyear deals with growth or efficiency incentives where possible to lock in long term costs. Self-handling gives Ryanair the option under European regulations to handle its own aircraft and passenger services where the company cannot obtain competitive rates or quality handling services at each airport. These contracts are generally scheduled to expire in one to five years, unless renewed. Ryanair will need to enter into similar agreements in any new markets it may enter.
Airport Charges
As with other airlines, Ryanair must pay airport charges each time it lands and accesses facilities at the airports it serves. Depending on the policy of the individual airport, such charges can include landing fees, passenger loading fees, security fees and parking fees. Ryanair attempts to negotiate discounted fees by delivering annual increases in passenger traffic and/or access to new destinations, and opts, when practicable, for less expensive facilities, such as less convenient gates and the use of outdoor boarding stairs rather than more expensive jetways.
Trademarks
Ryanair’s name, logo, certain other names and logos, as well as certain slogans, are registered as European Union Trademarks (‘EUTMs’) and as national trademarks in certain countries, including the U.K.
Trademarks owned by the Ryanair Group include:
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 18569159 consisted of the word ‘Ryanair’ in classes 16, 28, 35, 36, 39, 41, 42 and 43 (Nice Classification), and equivalent U.K. trademark number W00000001638372, protected until November 10, 2031.
European Union (Figurative) Trademark registration number 000338301 in classes 16, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39 and 42 (Nice Classification) and class 22.01.16 (Vienna classification), and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00900338301, protected until August 21, 2026.
European Union (Figurative) Trademark registration number 001493329 in classes 16, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39 and 42 (Nice Classification) and class 27.05.01 (Vienna classification), and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00901493329, protected until February 4, 2030.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 004187721 consisted of the word ‘Ryanairhotels.com’ in classes 16, 39 and 43 (Nice Classification), and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00904187721, protected until January 13, 2025.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 013185988 consisted of the word ‘LOW FARES. MADE SIMPLE’ in classes 16, 28, 35, 36, 37, 38, and 42 (Nice Classification), and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00913185988, protected until August 19, 2024.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 018295804 consisted of the word ‘Lauda Europe’ in classes 12, 16, 18, 25, 28, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 43 (Nice Classification) protected until August 25, 2030, and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00003680730, protected until August 12, 2031.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 003330685 consisted of the word ‘Laudamotion’ in classes 9, 14, 25, 35, 39 (Nice Classification) and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00903330685, protected until August 29, 2023.
European Union (Figurative) Trademark registration number 015102321 comprising in classes 3, 9, 14, 25, 35, 39 (Nice Classification) and classes 18.05.03, 27.05.22, 27.99.12, 27.99.13 (Vienna Classification) and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00915102321, protected until February 10, 2026.
European Union (Figurative) Trademark registration number 018062738 in classes 12, 16, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 43 (Nice Classification) and classes 03.13.04, 03.13.24, 27.05.21, 27.99.02 (Vienna Classification) protected until May 9, 2029, and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00003680736 protected until August 12, 2031.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 18018637 consisted of the word ‘BUZZAIR’ in classes 12, 16, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39 and 43 (Nice Classification) and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00003680696, protected until August 12, 2031.
The United Kingdom (Word) Trademark registration number UK00003247027 consisted of the word ‘Buzz About’ in class 39 (Nice Classification), protected until July 29, 2027.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 18018642 consisted of the word ‘BUZZ’ in classes 12, 16, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39 and 43 (Nice Classification) and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00003680711, protected until August 12, 2031.
European Union (Figurative) Trademark registration number 018409229 in classes 12, 35, 36, 39, 41, 43 (Nice Classification) and classes 04.01.03, 22.01.16, 24.17.20 (Vienna Classification) protected until February 26, 2031 and equivalent U.K. trademark number WO0000001606144, protected until April 26, 2031.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 18409226 in classes 12, 35, 36, 39, 41, 43 (Nice Classification) and classes 04.01.03 and 24.17.20 (Vienna Classification) protected until February 26, 2031 and equivalent U.K. trademark number 1606352, protected until April 26, 2031.
European Union (Combined) Trademark registration number 18569161 in classes 16, 28, 35, 36, 39, 41, 42 and 43 (Nice Classification) and class 24.11.25 (Vienna Classification) protected until September 30, 2031 and equivalent U.K. trademark number 1640512, protected until November 11, 2031.
European Union (Figurative) Trademark registration number 18569162 in classes 16, 28, 35, 36, 39, 41, 42 and 43 (Nice Classification) and class 24.11.25 (Vienna Classification) protected until September 30, 2031 and equivalent U.K. trademark number W00000001638371, protected until November 10, 2031.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 186977725 consisted of the word ‘MALTA AIR’ in classes 16, 28, 35, 36, 39, 41, 42 and 43 (Nice Classification), and equivalent U.K. trademark number W00000003784471, protected until May 5, 2032.
European Union (Figurative) Trademark registration number 186977728 in classes 16, 28, 35, 36, 39, 41, 42 and 43 (Nice Classification) and classes 24.13.4, 25.7.8, 26.3.4, 26.4.4, 26.4.5 and 29.1.1 (Vienna Classification) protected until May 5, 2032.
European Union (Logo) Trademark registration number 18723238 in classes 16, 28, 35, 36, 39, 41, 42 and 43 (Nice Classification) and classes 27.5.21 and 27.99.12 (Vienna Classification) protected until June 27, 2032 and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00003803577, protected until June 27, 2032.
European Union (Word) Trademark registration number 11220721 consisted of the word ‘Getaway Cafe’ in classes 29, 30, 32, 33 and 43 (Nice Classification), and equivalent U.K. trademark number UK00911220721, protected until September 27, 2032.
Strategy
The key elements of the company’s long-term strategy include stimulating demand, particularly from fare-conscious leisure and business travelers who might otherwise use alternative forms of transportation or choose not to travel at all; providing frequent point-to-point service on short- haul routes; taking advantage of digital platforms; enhancement of operating results through ancillary services; focused criteria for growth; and responding to market challenges. Ryanair’s strategy is to deliver the best customer service performance in its peer group. Safety is the primary priority of Ryanair.
Government Regulation
Regulatory Authorities
EU air carriers, such as the company and the Group Airlines are generally able to provide passenger services on domestic routes within any EU member state outside their home country, as well as between EU member states without restriction, subject to applicable EU and national regulations implemented by competent authorities, including the European Commission and EASA, as well as oversight by the European Organization for the Safety of Air Navigation (‘Eurocontrol’).
The Group Airlines are also subject to national regulation in their home countries, which is implemented primarily by in Ireland, the Irish Commission for Aviation Regulation (‘CAR’), the Irish Aviation Authority (‘IAA’) and the Irish Department of Transport (‘DoT’) in the case of Ryanair DAC; in Poland, the Polish Civil Aviation Authority (‘Polish CAA’) in the case of Buzz; in Malta, Transport Malta and the Maltese Civil Aviation Directorate (‘Maltese CAD’) in the case of Lauda Europe and Malta Air; and in the United Kingdom, the U.K. Civil Aviation Authority and the U.K. Department for Transport (‘U.K. DfT’) in the case of Ryanair U.K.
Ireland
Ryanair’s operating license (No 05/16) was issued by the CAR on September 20, 2016 and is subject to periodic review.
The IAA has broad authority to amend or revoke an AOC, with Ryanair’s ability to continue to hold its AOC being subject to ongoing compliance with current and future applicable statutes, rules and regulations pertaining to the airline industry. Ryanair DAC’s current AOC (No. IE 07/94) was issued by the IAA on January 11, 2022.
Malta
The company’s subsidiary, Malta Air, obtained an AOC (No. MT-57) and operating license (No. (CAD/MT-57) from the Maltese CAD on June 12, 2019.
The company’s subsidiary, Lauda Europe, obtained an AOC (No. MT-62) and operating license (No. (CAD/MT-62) from the Maltese CAD on September 4, 2020.
Poland
The company’s subsidiary Ryanair Sun S.A., operating as Buzz, obtained an AOC (No. PL-066) and operating license (No. ULC-LER-1/4000-0156/06/17) from the Polish CAA in April 2018.
The U.K.
The U.K. CAA has an authority to amend or revoke the AOC, with Ryanair U.K.’s ability to continue to hold its AOC being subject to ongoing compliance with applicable statutes. Ryanair U.K.’s flight operations, aircraft, maintenance facilities and air crew are subject to ongoing review and inspections by the U.K. CAA.
The company’s subsidiary, Ryanair U.K., obtained an AOC (No. GB 2451) and an operating license (OL/A/624) from the U.K. CAA on December 20, 2018.
Registration of Aircraft
The company’s aircraft operated by Malta Air and Lauda Europe are registered in Malta, the aircraft operated by Buzz are registered in Poland and the aircraft operated by Ryanair U.K. are registered in the U.K.
Regulation of Competition
Ryanair has been subject to an abuse-of-dominance investigation by the Irish Competition and Consumer Protection Commission in relation to service between Dublin and Cork. The Competition and Consumer Protection Commission (then known as the Competition Authority) closed its investigation in July 2009 with a finding in favor of Ryanair.
In December 2022, the Italian competition authority (the ‘AGCM’) launched an investigation into alleged illegal price coordination between airlines, including Ryanair, on routes between mainland Italy and Sicily during the Christmas period. The company has strongly refuted this allegation and is engaging with the AGCM whose investigation will likely conclude in late 2023 or early 2024.
Data Protection
Ryanair’s processing of personal data is subject to increasingly complex data protection laws, including the EU’s GDPR, as well as relevant national implementing legislation (Irish Data Protection Act 2018).
Environmental Regulation
Ryanair is subject to international, national and, in some cases, local noise regulation standards. EU and Irish regulations have required that all aircraft operated by Ryanair comply with Stage 3 noise requirements. All of Ryanair’s aircraft comply with these regulations. Certain airports in Ryanair’s network (including London Stansted, London Gatwick, Rome Ciampino, Dublin and Amsterdam) have established local noise restrictions, including limits on the number of hourly or daily operations or the time of such operations.
According to the Air Travel Carbon and Energy Efficiency Report published by Brighter Planet, Ryanair is the industry leader in terms of environmental efficiency, and the company is constantly working towards improving its performance.
Under Regulation 7 of The U.K. Companies Act 2006 (Strategic Report and Directors’ Report) Regulations 2013, Ryanair is obliged to state its annual quantity of emissions in tons of carbon dioxide equivalent. Ryanair’s EU and U.K. Emissions Trading Scheme monitoring, reporting and allowance surrender obligations are mandated on a calendar year basis.
Other
Health and occupational safety issues relating to Ryanair employees employed under Irish law are addressed in Ireland by the Safety, Health and Welfare at Work Act, 2005 (as amended) and other regulations under that Act. Although licenses or permits are not issued under such legislation, compliance is monitored by the Health and Safety Authority (the ‘Authority’), which is the regulating body in this area. The Authority periodically reviews Ryanair DAC’s health and safety record and when appropriate, issues improvement notices or prohibition notices. Ryanair DAC has responded to all such notices to the satisfaction of the Authority.
For Malta Air and Lauda Europe, health and occupational safety issues are addressed in the Maltese Occupational Health and Safety Authority Act XXVII of 2000.
Occupational health and safety issues relating to Ryanair U.K. are governed by various legislation, the primary statute in England being the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 (the ‘Health and Safety at Work Act’). The Health and Safety Executive (‘HSE’), monitors compliance with the Health and Safety at Work Act and related legislation.
History
Ryanair Holdings plc was founded in 1985. The company was incorporated in 1996.

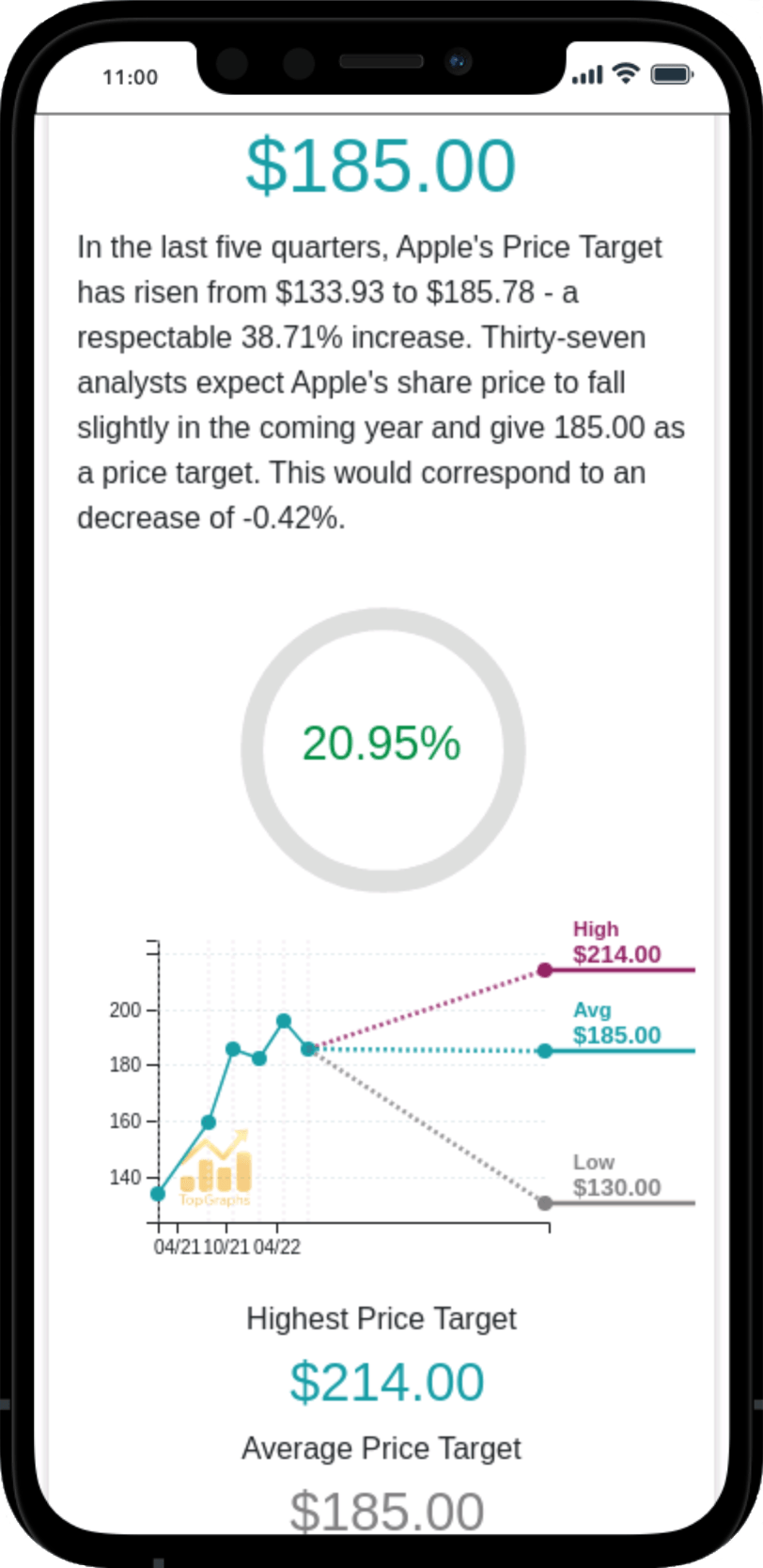
 Stock Value
Stock Value