About Pembina Pipeline
Pembina Pipeline Corporation (Pembina) is a leading energy transportation and midstream service provider that has served North America’s energy industry. The company owns an integrated network of hydrocarbon liquids and natural gas pipelines, gas gathering and processing facilities, oil and natural gas liquids infrastructure and logistics services, and an export terminals business. Through its integrated value chain, the company seeks to provide safe and reliable energy solutions that connect producers and consumers across the world, support a more sustainable future and benefit its customers, investors, employees and communities.
Divisions
The company operates through three divisions: Pipelines, Facilities, and Marketing & New Ventures.
Pipelines
The Pipelines Division provides customers with pipeline transportation, terminalling, storage and rail services in key market hubs in Canada and the United States for crude oil, condensate, natural gas liquids and natural gas. Through Pembina's wholly-owned and joint venture assets, the Pipelines Division manages pipeline transportation capacity of 2.8 thousands of barrels of oil equivalent per day (mmboe/d), above ground storage capacity of 11 mmbls and rail terminalling capacity of approximately 105 thousands of barrels of oil equivalent per day (mboe/d) within its conventional, oil sands and heavy oil, and transmission assets. The conventional assets include strategically located pipelines and terminalling hubs that gather and transport light and medium crude oils, condensate and natural gas liquids from western Alberta and northeast British Columbia to the Edmonton, Alberta area for further processing or transportation on downstream pipelines. The oil sands and heavy oil assets transport heavy and synthetic crude oil produced within Alberta to the Edmonton, Alberta area and offer associated storage, terminalling and rail services. The transmission assets transport natural gas, ethane and condensate throughout Canada and the United States on long haul pipelines linking various key market hubs. In addition, the Pipelines Division assets provide linkages between Pembina's upstream and downstream assets across North America, enabling integrated customer service offerings. Together, these assets supply products from hydrocarbon producing regions to refineries, fractionators and market hubs in Alberta, British Columbia, and Illinois, as well as other regions throughout North America.
Conventional Assets

Pembina's primary conventional assets include the following:
The Peace Pipeline system (Peace Pipeline), which includes approximately 4,000 km of pipelines, including gathering laterals, that transport ethane mix (C2+), propane mix (C3+), crude oil and condensate from northwestern Alberta to Edmonton, Alberta and to Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta.
The Northern Pipeline system (Northern Pipeline), which includes approximately 700 km of pipelines, including gathering laterals, that transport NGL from Belloy, Alberta to Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta.
Pembina continues to experience growing customer demand for transportation services to support development of the Montney, Duvernay and other resource plays and is undertaking an additional intra-Alberta expansion of the Peace Pipeline system. The Phase VIII Peace Pipeline expansion (Phase VIII Expansion), which includes 10-inch and 16-inch pipelines in the Gordondale to La Glace corridor, as well as six new pump stations or terminal upgrades located between Gordondale and Fox Creek, will add approximately 235,000 bpd of incremental capacity between Gordondale, Alberta and La Glace, Alberta, as well as approximately 65,000 bpd of capacity between La Glace, Alberta and the Namao hub near Edmonton, Alberta.
The Drayton Valley Pipeline system (Drayton Valley Pipeline), which includes approximately 1,100 km of pipelines, including gathering laterals, that transport crude oil and condensate from the area southwest of Edmonton, Alberta to Edmonton, Alberta.
The NEBC Pipeline system (NEBC Pipeline), which includes approximately 395 km of pipelines, including gathering laterals, that transport NGL, crude oil and condensate from northeastern British Columbia to Taylor, British Columbia.
The Western Pipeline system (Western Pipeline), which includes approximately 400 km of pipelines that transport crude oil from Taylor, British Columbia to Prince George, British Columbia.
The Liquids Gathering Pipeline system (LGS), which includes approximately 400 km of pipelines, including gathering laterals, that transport NGL from northeastern British Columbia to Gordondale, Alberta.
The Brazeau NGL Pipeline system (Brazeau Pipeline), which includes approximately 500 km of pipelines, including gathering laterals, that transport NGL from natural gas processing plants southwest of Edmonton, Alberta to Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta.
The Canadian Diluent Hub (Canadian Diluent Hub or CDH), which includes approximately 500 mbbls (thousands of barrels, each barrel representing 34.972 Imperial gallons or 42 U.S. gallons) of above ground storage and provides direct connectivity for domestic and the U.S. condensate volumes to the oil sands via downstream third-party pipelines.
The Edmonton North Terminal (ENT), which includes approximately 900 mbbls of above ground storage with access to crude oil and condensate supply transported on Pembina's operated pipelines and products from various third-party operated pipelines.
13 truck terminals, which provide pipeline and market access for crude oil and condensate production that is not pipeline connected.
There are approximately 65 shippers on the conventional pipeline systems owned and operated by Pembina, including independent producers and multinational oil and gas companies. The primary delivery points for hydrocarbon products from Pembina include the Enbridge pipeline systems for multiple products; Pembina's North 40 Terminal and the Trans Mountain pipeline system near Edmonton, Alberta; the Strathcona refinery in the Edmonton, Alberta area; Pembina's CDH near Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta; connected oil sands diluent pipelines; a refinery located in Prince George, British Columbia; the AEGS and all major NGL fractionators near Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta.
Pembina's conventional terminals are configured to access and provide services for the common grades of Canadian crude oil, as well as access domestic and imported condensate streams. The terminals provide essential services for Pembina's customers with outbound delivery flexibility and above ground storage.
At Pembina's truck terminals, the customer base generally comprises the same producers who seek to transport various products, including condensate, on Pembina's conventional and oil sands and heavy oil systems. Truck terminals are particularly attractive to producers who are unable to justify pipeline/oil battery connections due to relatively low daily production or are producing in advance of being pipeline connected.
The majority of crude oil, condensate and NGL product transported on the Peace Pipeline and Northern Pipeline systems are contracted under long-term, firm, take-or-pay contracts. As of December 31, 2022, the weighted average remaining term on Peace Pipeline and Northern Pipeline firm contracts was approximately eight years.
Services provided on other conventional assets and systems, such as the Drayton Valley Pipeline, LGS, Brazeau Pipeline, CDH, and ENT are generally under interruptible contracts.
Pembina's conventional pipelines are feeder pipelines that move products in the field from oil batteries, processing facilities and storage tanks to facilities, markets and export pipelines primarily in the Edmonton, Alberta and Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta areas. The majority of Pembina's conventional pipelines are connected to existing oil batteries and other facilities. Existing volumes generally remain connected to the applicable pipeline system until it is uneconomic to continue providing pipeline transportation services.
Oil Sands and Heavy Oil Assets
Pembina's primary oil sands and heavy oil assets include the following:
The Syncrude Pipeline system (Syncrude Pipeline), which includes approximately 450 km of pipelines, which have a capacity of 389 mbpd. Pembina is the sole transporter of synthetic crude oil for the Syncrude Project to delivery points near Edmonton, Alberta.
The Horizon Pipeline system (Horizon Pipeline), which includes approximately 525 km of pipelines, which have a capacity of 335 mbpd. Pembina transports synthetic crude oil for the Horizon Project to delivery points near Edmonton, Alberta.
The Cheecham Lateral system (Cheecham Lateral), which includes approximately 50 km of pipelines, which have a capacity of 230 mbpd and transports synthetic crude oil from a common pump station on the Syncrude Pipeline and Horizon Pipeline to a terminalling facility located near Cheecham, Alberta, where it is then used as diluent for oil sands producers operating southeast of Fort McMurray, Alberta.
The Nipisi Pipeline system (Nipisi Pipeline), which includes approximately 375 km of pipelines, was temporarily taken out of service in the fourth quarter of 2021 following contract expirations, but is expected to be reactivated to transport crude oil from the Clearwater formation to Edmonton, Alberta in the third quarter of 2023, with an anticipated capacity of approximately 100 mbpd.
The Swan Hills Pipeline (Swan Hills Pipeline), which includes an approximately 425 km pipeline, which has a capacity of 48 mbpd and provides transportation of light sweet crude oil from the Swan Hills region of Alberta to delivery points near Edmonton, Alberta.
The terminals at Edmonton, Alberta (the Edmonton Terminals), which consist of 36 merchant tanks with a capacity of approximately 12.1 mmbbls (9.6 mmbbls net to Pembina) of storage and a crude-by-rail capacity of 210 mbpd (105 mbpd net to Pembina). The terminals are connected to a highly diverse suite of inbound pipelines and outbound connections, including both pipeline and rail, resulting in the most robust connectivity in the Edmonton, Alberta area. The Edmonton Terminals include various joint venture assets with two different counterparties and are discussed below:
The Edmonton South Terminal (Edmonton South Terminal) is a merchant tank terminal located in Sherwood Park, Alberta. The assets in this facility consist of 15 storage tanks with a total storage capacity of approximately 5.1 mmbbls. The 15 tanks are leased from Trans Mountain Corporation under a long-term arrangement and are subleased to third parties.
The North 40 Terminal (North 40 Terminal) is a merchant tank terminal located in Sherwood Park, Alberta, immediately adjacent to the Edmonton South Terminal. The assets in this facility consist of nine storage tanks with a total storage capacity of approximately 2.15 mmbbls.
The Base Line Terminal (Base Line Terminal) is a joint venture asset owned by Pembina (50 percent) and Keyera (50 percent) and is operated by Pembina. It is a merchant crude oil storage terminal located on leased land at the Keyera, Alberta EnviroFuels facility in Sherwood Park, Alberta. The assets in this facility consist of 12 storage tanks with a total storage capacity of 4.8 mmbbls (2.4 mmbbl net to Pembina).
The Edmonton South Rail Terminal (Edmonton South Rail Terminal) is a joint venture asset owned by Pembina (50 percent) and Imperial (50 percent). The Edmonton South Rail Terminal is located on land leased from Imperial with a total throughput capacity of approximately 210 mbpd (105 mbpd net) and is unit train capable. The facility is served by both the Canadian National Railway and Canadian Pacific Railway networks.
The Edmonton Terminals assets provide excellent inbound and outbound connectivity, both in terms of the facilities to which they are connected and the diversity of products that may be stored and transported by them. In addition to the considerable market access offered to customers via pipeline, through their proximity and connectivity to crude-by-rail loading facilities, the Edmonton Terminals are able to offer customers the flexibility to move crude oil to markets without pipeline access, store or blend product, supplement deliveries to markets with constrained pipeline capacity, provide security of egress to manage product disruptions, and supply different or unique crude types to refineries looking to maintain set crude specifications.
The major shippers on Pembina's oil sands and heavy oil pipelines are primarily large upstream exploration and production companies.
Pembina's oil sands and heavy oil pipeline assets provide services predominantly under long-term, extendible contracts, which allow Pembina to pass along eligible operating expenses to customers. As a result, financial results of these assets are primarily driven by the amount of capital invested and they are not significantly impacted by fluctuations in certain operating expenses, physical throughput or commodity prices.
Pembina's Syncrude Pipeline is fully contracted under an extendible, long-term agreement that expires no earlier than the end of 2035.
The Horizon Pipeline is fully contracted to a single customer and is operated under the terms of a 25-year fixed return, extendible contract, which expires in 2034.
Pembina's Cheecham Lateral is fully contracted to shippers under the terms of 25-year fixed-return extendible agreements that expire in 2032.
The Swan Hills Pipeline is utilized by various shippers who transport mainly on an interruptible basis.
As a result of the contract expirations on the Nipisi Pipeline in the fourth quarter of 2021, the asset was taken out of service; however, Pembina is in the process of reactivating the Nipisi Pipeline to serve customers operating in the rapidly growing Clearwater formation. During the fourth quarter of 2022, Pembina executed agreements for a significant long-term commitment with an anchor customer, which includes the construction of a newly connected truck-in facility approximately 40 km north of Slave Lake, Alberta.
The Edmonton Terminals service customers consisting of a diverse mix of production, refining, marketing and integrated companies. The Edmonton Terminals are primarily contracted under long-term, take-or-pay agreements. A significant majority of total revenue from the Edmonton Terminals is take-or-pay in nature, while the remaining revenue is derived from variable fees for incremental services provided.
Transmission Assets
Pembina's primary transmission assets include the following:
Vantage Pipeline
The Vantage Pipeline system (Vantage Pipeline) includes a 786 km, 69 mbpd pipeline and gathering laterals that link ethane supply from the Bakken resource play in North Dakota to the petrochemical market in Alberta. Volumes originate from two gas plants in Tioga, North Dakota extending northwest through Saskatchewan and terminating near Empress, Alberta, where it is connected to the AEGS.
Transportation service on the Vantage Pipeline is underpinned by long-term, fee-for-service contracts with take-or-pay provisions. The Vantage Pipeline contracts are with one customer with petrochemical infrastructure in Alberta, with multiple receipt points along the Vantage Pipeline. Approximately 50 percent of the Vantage Pipeline's capacity is contracted on a take-or-pay basis with additional volumes flowing on a fee-for-service basis, with current contracts expiring between 2029 and 2035.
Alberta Ethane Gathering System
The Alberta Ethane Gathering System (AEGS) transports ethane within Alberta from various ethane extraction plants to major petrochemical complexes located near Joffre, Alberta and Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta. At 1,336 km in total length, and an aggregate design capacity of approximately 330 mbpd, the AEGS consists of an east leg, west leg and a bi-directional north leg, which together form an integrated system, that includes interconnections with underground storage sites in Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta and Burstall, Saskatchewan.
The AEGS shipper community consists of either major ethane producers or consumers that have significant energy infrastructure and/or petrochemical investments in Alberta. The AEGS is fully contracted with nearly 100 percent of its capacity contracted under 20-year take-or-pay agreements expiring in 2038.
Alliance Pipeline
The Alliance Pipeline system (Alliance Pipeline) is held through Alliance Canada and Alliance U.S., both of which are jointly owned by Pembina (50 percent) and by Enbridge Inc. (50 percent).
The Alliance Pipeline consists of a 3,849 km integrated Canadian and U.S. natural gas transmission pipeline, delivering rich gas from the WCSB and the Williston Basin in North Dakota to natural gas markets in the Chicago, Illinois area and delivers an average of 1.7 billion cubic feet per day (bcf/d) of rich gas. The Alliance Pipeline connects to Aux Sable's Channahon Facility in Channahon, Illinois, which extracts NGL from the natural gas transported before delivery to downstream pipelines.
Several open seasons were successfully completed in 2022, resulting in capacity on the Alliance Pipeline being nearly fully contracted for the two gas years, beginning November 1, 2022 and November 1, 2023, respectively. As a result of the open seasons and contract renewal efforts, approximately 70 percent of the Alliance Pipeline capacity is contracted for the following two gas years, beginning November 1, 2024 and November 1, 2025.
The Canadian portion of the Alliance Pipeline consists of a 1,561 kilometres (km) natural gas mainline pipeline and 732 km of related lateral pipelines connected to natural gas receipt locations, primarily at gas processing facilities in northwestern Alberta and northeastern British Columbia, and related infrastructure. Alliance Canada owns the Canadian portion of the Alliance Pipeline.
The U.S. portion of the Alliance Pipeline consists of 1,556 km of infrastructure, including the 129 km Tioga lateral in North Dakota. Alliance U.S., an affiliate of Alliance Canada, owns the U.S. portion of the Alliance Pipeline system.
As of December 31, 2022, Alliance Canada had 29 long-term firm shippers and Alliance U.S. had 26 long-term firm shippers. Firm transportation contracts are take-or-pay and shippers are obligated to pay demand charges on contracted capacity in Canada and reservation charges on contracted capacity in the U.S. In addition, Alliance Canada sells seasonal firm and interruptible transportation service on a price-biddable basis. Long-term firm receipt and full path shippers in Canada are also able to nominate priority interruptible transportation service for up to 25 percent of their contracted capacity, if available, at premiums to their long-term firm tolls.
The Alliance Pipeline faces competition for pipeline transportation services to its Chicago, Illinois area delivery points and interconnected pipeline delivery points downstream of its Chicago terminus from both existing pipelines and proposed projects. The Alliance Pipeline system is also exposed to competition from new sources of natural gas, such as the Appalachian Basin which runs from upstate New York to Virginia. The continued development of the Appalachian Basin may provide an alternative source of gas to the Chicago, Illinois area and decrease natural gas imports from Canada into the region.
Cochin Pipeline
The Cochin Pipeline system (Cochin Pipeline) consists of a 12-inch diameter pipeline totaling 2,452 km, which spans from Kankakee County, Illinois to Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta. The Cochin Pipeline, transports light condensate primarily to be used as diluent to facilitate bitumen transportation. The Cochin Pipeline traverses two provinces in Canada and four states in the U.S. and is capable of transporting approximately 110 thousands of barrels per day (mbpd) of light condensate.
The Cochin Pipeline has two primary customers who, among them, have total contractual take-or-pay commitments of 85 mbpd. These contractual commitments expire in 2024. An open season was completed in January 2023 with 9,000 bbls/d of capacity contracted for 12 to 17 months commencing March 1, 2023.
Condensate used in Canada is primarily supplied by local production and imports from the U.S. While the Cochin Pipeline is exposed to competition from other pipeline systems that are capable of transporting significant volumes of diluent, the Cochin Pipeline's delivery point in Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta has a low gravity diluent pool and a high level of connectivity, thereby making the Cochin Pipeline an attractive mode of shipping condensate.
Ruby Pipeline
The Ruby Pipeline system (Ruby Pipeline) is a natural gas transmission system delivering natural gas production from the Rockies Basin. The Ruby Pipeline is 1,094 km in length with a 42-inch diameter and has a capacity of 1.5 bcf/d.
The Ruby Subsidiary had U.S. $475 million principal amount of unsecured notes that matured on April 1, 2022 (the Ruby Subsidiary Notes). On March 31, 2022, the Ruby Subsidiary filed a voluntary petition for relief under Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the District of Delaware (the Ruby Subsidiary Bankruptcy). On November 18, 2022, Pembina and certain of its subsidiaries entered into the Ruby Settlement Agreement with the Ruby Subsidiary which provides for the release of Pembina from any causes of action arising in connection with, among other things, the prepetition distributions and the Ruby Subsidiary Bankruptcy. In January 2023, the United States Bankruptcy Court for the District of Delaware approved the Ruby Subsidiary's Chapter 11 plan of reorganization (the Ruby Subsidiary Plan) and the Ruby Settlement Agreement. The Ruby Subsidiary Plan provides for the sale of the Ruby Subsidiary's reorganized equity to a third-party, which sale was completed on January 13, 2023, and the distribution of the sales proceeds and cash on hand of the Ruby Subsidiary to the creditors of the Ruby Subsidiary, including a certain affiliate of Pembina in respect of the subordinated notes issued by the Ruby Subsidiary to that Pembina affiliate.
Jet Fuel Pipeline
The Jet Fuel Pipeline (Jet Fuel Pipeline) is an approximately 40 km pipeline that transports jet fuel from a Burnaby, British Columbia refinery and the Westridge Marine Terminal to the Vancouver International Airport and includes operational storage tanks at the Vancouver International Airport. On April 30, 2021, the Jet Fuel Pipeline was shutdown in order to address certain integrity issues. The work required to address these integrity issues was completed in accordance with a return to service plan agreed to with the applicable regulatory agencies and the Jet Fuel Pipeline returned to service on June 30, 2022 with an operational capacity of 15 mbpd.
Grand Valley
Grand Valley (Grand Valley) includes Pembina's 75 percent jointly controlled interest in Grand Valley 1 Limited Partnership wind farm.
Facilities division
The Facilities division includes infrastructure that provides Pembina's customers with natural gas, condensate and NGL services. Through its wholly-owned assets and its interest in PGI, Pembina's natural gas gathering and processing facilities are strategically positioned in active, liquids-rich areas of the WCSB and Williston Basin and are integrated with the company's other businesses. Pembina provides sweet and sour gas gathering, compression, condensate stabilization, and both shallow cut and deep cut gas processing services with a total capacity of approximately 5.4 bcf/d for its customers. Condensate and NGL extracted at virtually all Canadian-based facilities have access to transportation on Pembina's pipelines. In addition, all NGL transported along the Alliance Pipeline are extracted through the Pembina operated Channahon Facility at the terminus. The Facilities Division includes approximately 354 mbpd of NGL fractionation capacity, 21 mmbbls of cavern storage capacity and associated pipeline and rail terminalling facilities and a liquefied propane export facility on Canada's West Coast. These facilities are fully integrated with the company's other divisions, providing customers with the ability to access a comprehensive suite of services to enhance the value of their hydrocarbons. In addition, Pembina owns a bulk marine import/export terminal in Vancouver, British Columbia.
Gas Services
Pembina's primary gas services assets include the following:
Pembina's 60 percent operating interest in PGI, which has ownership interests in the following assets as noted below:
The Saturn Gas Plant (100 percent), Sunrise Gas Plant (100 percent) and Tower Gas Plant (100 percent) (collectively, the Dawson Assets), which have combined gross processing capacity of 1,100 MMcf/d (660 MMcf/d net to Pembina). These assets also include approximately 800 km of gas gathering lines and three liquids hubs.
The Cutbank Complex (the Cutbank Complex) located near Grande Prairie, Alberta, which includes four shallow cut sweet gas processing plants (the Cutbank Gas Plant (100 percent), Musreau I (89 percent) comprised of three trains, Musreau II/III (100 percent) comprised of two trains, and the Kakwa 1-35 Gas Plant (50 percent)), and one deep cut sweet gas processing plant (the Musreau Deep Cut (100 percent)). In total, the Cutbank Complex has 805 MMcf/d (449 MMcf/d net to Pembina) of sweet gas processing capacity including 205 MMcf/d (123 MMcf/d net to Pembina) of sweet deep cut extraction capacity. The Cutbank Complex also includes approximately 450 km of gathering pipelines, nine field compression stations, and centralized condensate stabilization.
The Hythe Gas Plant (100 percent) and Steeprock Gas Plant (100 percent), which are located Northwest of Grande Prairie, Alberta with sweet and sour gas processing capacity of 641 MMcf/d (385 MMcf/d net to Pembina). The plants have approximately 480 km of associated gathering lines.
The Saturn Complex (the Saturn Complex), which is located near Hinton, Alberta and includes the Saturn I (100 percent) and Saturn II (100 percent) facilities for a total of 435 MMcf/d (261 MMcf/d net to Pembina) of deep cut gas processing capacity, as well as approximately 25 km of gathering pipelines.
The Patterson Creek Plant (98 percent) (Patterson Creek), which is a sweet gas processing facility located southeast of Grande Prairie, Alberta with shallow cut NGL recovery. Patterson Creek has an operational capacity of 390 MMcf/d (230 MMcf/d net to Pembina), as well as 482 km of gathering pipelines.
The Kaybob South 3 Processing Plant (97 percent) (the K3 Plant), which is located south of Fox Creek, Alberta, is a sour gas processing facility with shallow cut NGL recovery. The K3 Plant has an operational capacity of 375 MMcf/d (218 MMcf/d net to Pembina), as well as 751 km of gathering pipelines.
The Duvernay Complex (the Duvernay Complex) located near Fox Creek, Alberta, which includes three shallow cut sweet gas processing trains (Duvernay I (92 percent), Duvernay II (92 percent) and Duvernay III (92 percent)), the Duvernay Sour Treating Facilities and the Duvernay Field Hub. In total, the Duvernay Complex has 330 MMcf/d (182 MMcf/d net to Pembina) shallow cut sweet gas processing trains, 330 MMcf/d of inlet gas handling capability, 60 mbpd of raw inlet condensate stabilization facilities, 15 mbpd of water handling facilities, a 150 MMcf/d sour gas sweetening system with 300 MMcf/d of amine regeneration capability and up to one tonne of sulphur per day of acid incineration. Supporting infrastructure includes a 12 km sales gas pipeline and 35 km of gas gathering and fuel gas pipelines.
The Resthaven Facility (78 percent) (the Resthaven Facility), which is located near Grande Cache, Alberta and includes 300 MMcf/d (141 MMcf/d net to Pembina) of raw-to-deep cut sweet gas processing capacity, as well as approximately 30 km of gathering pipelines.
The Kakwa River facility (100 percent), which has 200 MMcf/d (120 million cubic feet per day (mmcf/d) net to Pembina) of raw-to-deep cut sour gas processing capacity (the Kakwa River Deep Cut Plant) and 50 mmcf/d (30 mmcf/d net to Pembina) of shallow cut capacity (the Kakwa River Shallow Cut Plant).
The Kaybob South Amalgamated Plant (90 percent) (the KA Plant), which is a sour gas processing facility located southwest of Fox Creek, Alberta with shallow cut NGL recovery. The KA Plant has an operational capacity of 220 MMcf/d (119 MMcf/d net to Pembina) and includes 239 km of gathering pipelines.
The Wapiti Plant (100 percent) (the Wapiti Plant), which is a sour gas processing facility located southwest of Grande Prairie, Alberta with shallow cut NGL recovery. The Wapiti Plant has an operational capacity of 200 MMcf/d (120 MMcf/d net to Pembina) and includes 420 km of gathering pipelines.
The Smoke Lake Plant (100 percent), which is a gas processing facility located near Fox Creek, Alberta with a capacity of 60 MMcf/d (36 MMcf/d net to Pembina).
The Saskatchewan Ethane Extraction Plant (100 percent) (SEEP), which is located near Viewfield, Saskatchewan and services producers in the Bakken formation in southeast Saskatchewan, with deep cut sweet gas processing capacity of 54 MMcf/d (32 MMcf/d net to Pembina), ethane, propane and butane fractionation capabilities of up to 4.5 mbpd and a 104 km ethane delivery pipeline.
The Younger NGL Extraction Facility (Younger), which is a 640 MMcf/d (459 MMcf/d net to Pembina) extraction facility and approximately 10 mbpd, net to Pembina, fractionation facility in British Columbia that supplies specification NGL products to local markets, as well as NGL mix supply transported on the company's pipeline systems to the Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta area for fractionation and sale, and condensate to Pembina's CDH.
The Empress NGL Extraction Facility (Empress), which consists of 1,200 MMcf/d (1,065 MMcf/d net to Pembina) of extraction capacity and 67 mbpd, net to Pembina, of ethane-plus fractionation across various joint-venture assets and is located at Empress, Alberta. At Empress, NGL mix is extracted from natural gas at straddle plants and all of the extracted NGL is fractionated and ethane and condensate are sold into western Canadian markets. The remaining propane and butane, at Pembina's option is either distributed for sale into western Canadian and mid-western U.S. markets or Pembina recombines the propane and butane and transports the mix to Sarnia, Ontario for further re-fractionation, distribution and sale into markets in eastern Canada and the eastern U.S. The Empress Co-generation Facility (the Empress Co-generation Facility) was placed into service on November 8, 2022 and uses natural gas to generate up to 45 megawatts of electrical power.
Burstall Ethane Storage (Burstall), which consists of an ethane storage facility, with capacity of 1.1 mmbbls, located near Burstall, Saskatchewan.
Pembina's gas services business has approximately 65 customers, including independent producers as well as multinational oil and gas companies. Pembina processes customers' natural gas at PGI's Cutbank Complex, Saturn Complex, Resthaven Facility, Duvernay Complex, Dawson Assets, Hythe Gas Plant, Steeprock Gas Plant, K3 Plant, KA Plant, Patterson Creek, and the Wapiti Plant. The processed natural gas is delivered to Enbridge Inc.'s T-North system in British Columbia, NOVA Gas Transmission Ltd.'s pipeline system and the Alliance Pipeline system. The processed NGL are delivered to Pembina's Peace Pipeline and Northern Pipeline systems. Customers' natural gas processed at SEEP is delivered to the TransGas system in Saskatchewan and the ethane is delivered to Pembina's Vantage Pipeline system.
Duvernay I and the associated Duvernay Field Hub connecting the Tony Creek and Fox Creek areas in Alberta are subject to agreements with large and diversified investment grade oil and gas producers and are supported by a combination of fee-for-service, fixed return and take-or-pay arrangements. The Duvernay II, Duvernay III and Duvernay Sour Gas Treating Facilities are supported by 20-year contracts with a combination of fee-for-service, fixed-return and take-or-pay arrangements. Contract expirations for the Duvernay Complex range from 2024 to 2040, with the majority of contracted capacity expiring in 2039 and 2040.
The Dawson Assets are supported by fee-for-service agreements with the CRP and Ovintiv, whereby the CRP has committed to use the Dawson Assets on an exclusive basis for a 30-year term within an area of mutual interest. The contract expires in 2045.
The Hythe Gas Plant and Steeprock Gas Plant are supported by a cost of service-agreement and take-or-pay arrangements with Ovintiv for the majority of the available capacity of these facilities. The majority of contracted capacity expires in 2031.
Pembina's net share of capacity at Younger and Empress are not under any third-party contracts and are used exclusively by Pembina's marketing business for proprietary volumes.
With its existing assets, Pembina is able to separate crude oil and condensate, process sweet and sour gas, extract NGL from the gas, transport the gas to the Chicago, Illinois area and transport the liquids through its conventional pipelines to its CDH, ENT, Edmonton Terminals and fractionation complexes, where Pembina is able to market the products to end users.
Pembina's gas services business is subject to competition from other gas processors, producer owned infrastructure and to a lesser degree, the Alliance Pipeline which is a high heat content gas egress option.
NGL Services
Pembina's primary NGL services assets include the following:
The fractionation and storage facilities (Redwater Complex), which includes: two 73 mbpd ethane-plus fractionators (being RFS I and RFS II, respectively); a 55 mbpd propane-plus fractionator (RFS III); and 12.1 millions of barrels (mmbbls) of cavern storage located in Redwater, Alberta. The Redwater Complex purchases NGL mix from various natural gas and NGL producers and fractionates it into finished products for further distribution and sale. Pembina sanctioned construction of a new 55 mbpd propane-plus fractionator (RFS IV) at the Redwater Complex. Subject to regulatory and environmental approvals, RFS IV is expected to be in-service in the first half of 2026. With the addition of RFS IV, the fractionation capacity at the Redwater Complex will total 256 mbpd.
The East NGL System (East NGL System), which includes:
Up to 20 mbpd of fractionation capacity and 1.2 mmbbls of cavern storage in Sarnia, Ontario;
Storage and terminalling assets/capacity at Kerrobert, Saskatchewan, and Superior, Wisconsin; and
6 mmbbls of hydrocarbon storage, truck and rail loading facilities at Corunna, Ontario.
The Prince Rupert Terminal (the Prince Rupert Terminal), a propane export terminal located on Watson Island, British Columbia on lands leased from a wholly-owned subsidiary of the city of Prince Rupert. The Prince Rupert Terminal is a small-scale rail terminal, moving propane from rail cars to pressurized storage spheres, and ultimately to 'handysize' vessels destined for international markets. The Prince Rupert Terminal was placed into service at the end of the first quarter of 2021 and has a capacity of approximately 20 mbpd.
The Vancouver Wharves (Vancouver Wharves), located in North Vancouver, B.C., is a 125-acre bulk marine terminal facility that in 2022 transferred over 4 million tons of bulk cargo and 5.3 mmbbl of liquids predominantly to offshore export markets. The Vancouver Wharves are operated under an operating lease and asset ownership agreement with the B.C. Railway Company and a corresponding water lot lease with Port Metro Vancouver. The terminal includes one million tons of bulk storage capacity, 450,000 barrels of distillate storage capacity, four berths, facilities that can house up to 325 rail cars and connectivity to three Class 1 rail companies.
A 50 percent interest in Fort Corp, which has 27,500 metric tonnes of ethylene storage and 33,400 metric tonnes of ethane-plus NGL mix storage near Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta.
Pembina's NGL service business provides a multitude of services for its customers. It is common practice for customers to sign up for more than one service with Pembina, including fractionation, storage, loading and off-loading.
At the Redwater Complex, Pembina provides NGL fractionation, storage and terminalling (loading and off-loading) services. NGL fractionation services at the Redwater Complex are provided under single or multi-year, predominately take-or-pay contracts. Pembina also provides third party terminalling services at the Redwater Complex for the Sturgeon Refinery, which is operated by the Northwest Redwater Limited Partnership under a long-term fixed-return agreement.
Through its East NGL System, Pembina provides NGL fractionation, storage and terminalling (loading and off-loading) services in Superior, Wisconsin and Sarnia, Ontario primarily on an interruptible, fee-for-service basis to Pembina's Marketing & New Ventures Division. Pembina also provides storage and terminalling services in Corunna, Ontario on both fee-for-service and fixed-return agreements, on an annual and multi-year basis, to third party customers and Pembina's Marketing & New Ventures Division.
The Prince Rupert Terminal provides export of propane produced in Western Canada for delivery into international propane markets. The terminal primarily provides service on a fee-for-service basis to Pembina's Marketing & New Ventures Division and their customers.
Vancouver Wharves capacity is contracted under long-term, take-or-pay terminal service agreements. Some of Pembina's major long-term contracts at the Vancouver Wharves are extendible.
Marketing & New Ventures division
The Marketing & New Ventures Division strives to maximize the value of hydrocarbon liquids and natural gas originating in the basins where the company. In particular, Pembina seeks to identify opportunities to connect hydrocarbon production to new demand locations through the development of infrastructure. Pembina strives to increase producer netbacks and product demand to improve the overall competitiveness of the basins where the company operates.
Marketing Activities
Within the Marketing & New Ventures Division, Pembina undertakes value-added commodity marketing activities, including buying and selling products (natural gas, ethane, propane, butane, condensate, crude oil and electricity), commodity arbitrage, and optimizing storage opportunities. The marketing business enters into contracts for capacity on both Pembina's and third-party infrastructure, handles proprietary and customer volumes and aggregates production for onward sale. Through this infrastructure capacity, as well as utilizing the company's expansive rail fleet and logistics capabilities, Pembina's marketing business adds incremental value to the commodities by accessing high value markets across North America and globally.
The value potential associated with Pembina's marketing business is dependent upon, among other things, Pembina's ability to: access connections to both downstream pipelines and end-use markets; understand the value of the commodities transported, stored and terminalled; provide flexibility and a variety of storage options; and adjust to a liquid, responsive, forward commodity market. Pembina actively monitors market conditions and commodity stream values and qualities to target revenue opportunities and service offerings. Pembina is also proactively working with upstream and downstream customers to develop value-added terminalling solutions and increase available optionality.
Customers within Pembina's marketing business are generally those who produce, consume and/or market crude oil, NGL, natural gas and electricity, are downstream markets for those products, or are interested in ancillary services related to those products. Pembina's marketing business leverages the company's integrated value chain, focusing on activities that complement the existing network of facilities and energy infrastructure across Pembina's asset base.
The contractual arrangements associated with Pembina's marketing business vary by service offering.
Aux Sable
Pembina's ownership interest in Aux Sable (Aux Sable), which includes Aux Sable Canada and Aux Sable U.S., is included in the Marketing & New Ventures Division, since the majority of cash flow from this asset is derived from commodity sales. Pembina is the operator of the Aux Sable assets.
Aux Sable U.S. (Aux Sable U.S.) consists of Aux Sable Liquids Products Inc., Aux Sable Liquid Products LP (Aux Sable U.S. LP) and Aux Sable Midstream LLC. Collectively Aux Sable U.S. is owned by Pembina (42.7 percent), indirectly by Enbridge Inc. (42.7 percent) and indirectly by Williams Partners (14.6 percent). The primary assets of Aux Sable U.S. include:
The Channahon Facility (Channahon Facility), located in Channahon, Illinois, about 80 km southwest of Chicago near the eastern terminus of the Alliance Pipeline. The Channahon Facility is capable of processing 2.1 bcf/d of natural gas and can produce approximately 131 mbpd of specification NGL products. All of the natural gas delivered via the Alliance Pipeline is processed at the Channahon Facility.
The Channahon Facility includes storage and rail facilities, as well as NGL pipelines that connect the facility to various third-party terminals, refineries and petrochemical plants. The scale and geographic location of the Channahon Facility provides producers located in Western Canada and North Dakota with economic options for liquids rich gas takeaway and access to U.S. NGL markets, avoiding costly investments in field processing and transportation infrastructure.
The Palermo Conditioning Plant (Palermo Conditioning Plant), located near Palermo, North Dakota, a 80 MMcf/d plant, which receives gas from gathering systems servicing nearby Bakken shale oil and gas production areas and removes the heavier hydrocarbon compounds while leaving the majority of the natural gas liquids in the rich gas prior to shipping on the Alliance Pipeline via delivery on the Prairie Rose Pipeline.
The Prairie Rose Pipeline (Prairie Rose Pipeline), a 120 MMcf/d pipeline connecting the Palermo Conditioning Plant to the Alliance Pipeline.
Under transportation agreements with natural gas shippers on the Alliance Pipeline, Aux Sable U.S. LP has the right to extract NGL from all of the natural gas transported for the durations of the applicable agreements. Aux Sable has signed NGL value-sharing agreements with certain gas producers in Alberta, British Columbia and North Dakota.
Aux Sable U.S. LP entered into an exclusive NGL sale agreement with an NGL marketer on December 31, 2005, pursuant to which Aux Sable U.S. LP sells a portion of its NGL production from the Channahon Facility to such counterparty. In return, Aux Sable U.S. LP receives a fixed annual fee and percentage share of any net margin generated from the business in excess of specified thresholds. The NGL sales agreement has an initial term expiring March 31, 2026 and may be extended for subsequent 10-year terms.
Aux Sable Canada (Aux Sable Canada) consists of Aux Sable Canada LP and Aux Sable Canada Ltd. Aux Sable Canada is owned by Pembina (50 percent) and indirectly by Enbridge Inc. (50 percent). The primary assets of Aux Sable Canada include:
The Heartland Offgas Plant (HOP), a 20 MMcf/d extraction plant located in Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta. HOP produces valuable products including hydrogen, ethane, and other natural gas liquids from a refinery offgas stream supplied from Shell's Scotford Complex. The products are returned to Shell via pipeline.
The Septimus Pipeline (Septimus Pipeline), which is located in northeastern British Columbia and transports sweet, liquids rich gas from the Septimus and Wilder gas plants to the Alliance Pipeline, for downstream processing at Aux Sable U.S.'s Channahon Facility. The Septimus Pipeline is 100 percent owned by Aux Sable Canada and operated by a third-party and has a capacity of approximately 350 MMcf/d.
New Ventures
The Marketing & New Ventures division is also responsible for the development of new large-scale, or value chain extending projects, including those that provide enhanced access to global markets and support a transition to a lower-carbon economy. Pembina is pursuing opportunities associated with LNG, low-carbon commodities, and large-scale GHG emissions reductions.
Cedar LNG
Pembina has formed a partnership with the Haisla First Nation to develop the proposed Cedar LNG Project, a three million tonne per annum floating LNG facility strategically positioned to leverage Canada's abundant natural gas supply and British Columbia's growing LNG infrastructure to produce industry-leading low-carbon, Canadian LNG for overseas markets. Cedar LNG will provide a valuable outlet for WCSB natural gas to access global markets, achieving higher prices for Canadian producers, contributing to lower overall emissions, and enhancing global energy security. Given Cedar LNG will be a floating facility, manufactured in the controlled conditions of a shipyard, it is expected that the project will have lower construction and execution risk. Further, powered by BC Hydro, Cedar LNG is expected to be one of the greenest LNG facilities in the world. The Environmental Assessment (EA) was referred to the B.C. Ministers of Environment and Energy and Mines on November 16, 2022, and the decisions of the B.C. Ministers as well as the federal Minister of Environment and Climate Change are expected to be received in the first quarter of 2023.
As with most of Pembina's assets, Cedar LNG is expected to be structured as a tolling business providing a low risk, long-term cash flow stream, and strengthening Pembina's financial guardrails. Cedar LNG is in active commercial discussions with potential counterparties, all of which are investment grade, for long-term commitments, and is working towards the signing of definitive agreements prior to a final investment decision. Work with EPC contractors in the development of the floating LNG Facility continues.
Alberta Carbon Grid
Pembina and TC Energy continue to develop the Alberta Carbon Grid, a carbon transportation and sequestration platform that will enable Alberta-based industries to effectively manage their greenhouse gas emissions, contribute positively to Alberta's lower-carbon economy, and create sustainable long-term value for Pembina and TC Energy stakeholders. In 2022, the Government of Alberta announced that the Alberta Carbon Grid was successfully chosen to move to the next stage of the province's carbon capture utilization and storage process in the Industrial Heartland. Throughout the year, Pembina and TC Energy progressed surface and sub-surface engineering and planning, continued with ongoing engagement with customers and stakeholders, and recently signed an evaluation agreement with the Government of Alberta. The first phase of the system is the Industrial Heartland project, which will have the potential of transporting and storing up to 10 million tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) annually. Pembina and TC Energy are also exploring options to create several hubs throughout Alberta. The long-term vision is to annually transport and store up to 20 million tonnes of CO2 through several hubs across Alberta.
Chinook Pathways Partnership
Pembina has been chosen by the Western Indigenous Pipeline Group to be the industry partner in the formation of Chinook Pathways, an Indigenous-led partnership working to organize a significant number of First Nation communities to pursue ownership of the Trans Mountain Pipeline following completion of the construction of the Trans Mountain Expansion.
Seasonality
Pembina's businesses are affected by seasonality in the following ways:
Pembina typically experiences higher pipeline maintenance and integrity spending in the first and fourth quarters of the year (year ended December 31, 2022). Labour productivity may be negatively impacted by seasonal weather conditions, including extreme temperatures in the winter.
Conventional feeder pipelines and gathering systems generally experience lower volumes during the spring months as a result of reduced drilling primarily due to weight restrictions on roads, producers conducting maintenance on their batteries and gas plant turnarounds. The magnitude and duration of road weight restrictions are dependent upon spring weather conditions.
Volumes transported on the Alliance Pipeline or volumes processed at gas processing facilities are generally higher during winter months as gas compression is more efficient in cold weather and there is, therefore, increased availability to flow interruptible volumes in the winter months, subject to customer demand for the service.
Environmental Matters and Environmental Stewardship
Pembina participates in various applicable regulated emission reporting programs, such as Canadian Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program, Canadian National Pollutant Release Inventory Reporting, Alberta Specified Gas Reporting Regulation, Alberta Technology, Innovation and Emission Reduction Regulation, British Columbia Greenhouse Gas Emission Reporting Regulation, Saskatchewan Management and Reduction of Greenhouse Gases (Reporting) Regulation, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Greenhouse Gas Report, as well as other provincial and state air quality reporting requirements under asset-specific approval conditions.
Pembina is subject to regulation by the Alberta Energy Regulator (AER) under the AER's liability management framework, including the Licensee Management Program, the Inventory Reduction Program, the Licensee Liability Rating Program and the Large Facility Liability Management Program. As of December 1, 2021, AER Directive 088: Licensee Life-cycle Management (Directive 088) came into force and will replace the AER's current Licensee Liability Rating Program over time. Directive 088 institutes a wholistic assessment regime with several different regulatory tools not limited to the current use of security deposits. This wholistic regime applies to licence transfers and has implemented the Inventory Reduction Program. Under the Inventory Reduction Program, which became effective on January 1, 2022, all licensees that have liability associated with inactive infrastructure are required to spend a specified amount each year on reclamation activities, or post equivalent security with the AER.
Pembina's other CER-regulated pipelines are classified as Group 2 by the CER. For these Group 2 pipeline systems, if no complaint is filed, the CER may presume that the filed tariffs are just and reasonable. The Northwest Pipeline, the Taylor to Belloy Pipeline, the Pouce Coupe Pipeline and the Pouce Coupe Lateral, all licensed by Pembina's wholly-owned subsidiary Pouce Coupe Pipe Line Ltd., are regulated by the CER. Pembina's Taylor to Boundary Lake Pipeline, which is owned by Pembina Energy Services Inc., Pembina's Vantage Pipeline, which is owned by Pembina Prairie Facilities Ltd., and Pembina's Empress Pipeline, which is owned by Veresen NGL Pipeline Inc., all wholly-owned subsidiaries of Pembina, are also regulated by the CER. The four pipelines collectively referred to as the Tupper Pipelines, licensed by Veresen Energy Pipeline Inc., and 60 percent owned by Pembina, are also regulated by the CER. The Kerrobert pipeline is regulated by the CER but is not operated by Pembina.
History
Pembina Pipeline Corporation was founded in 1954.

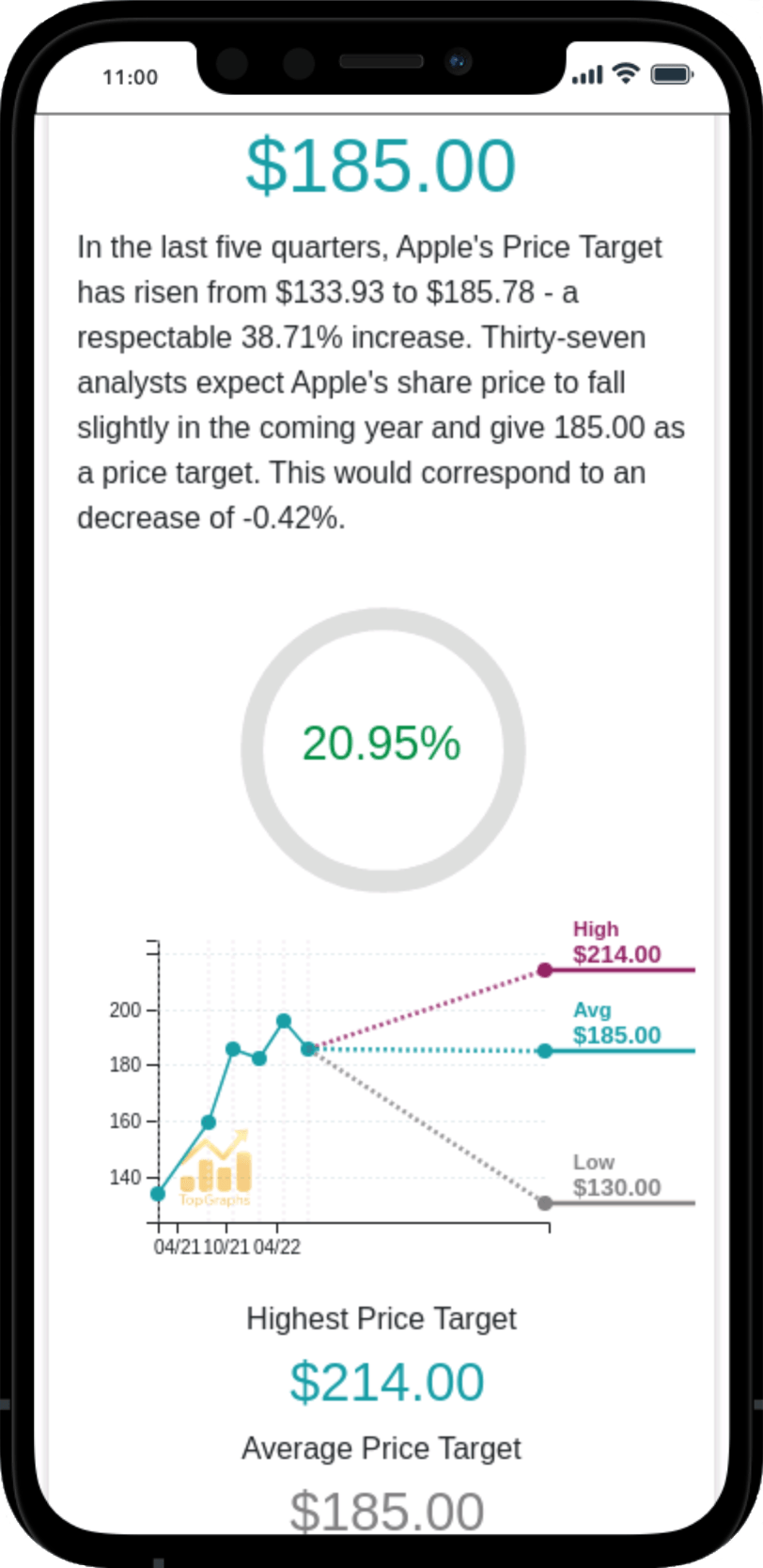
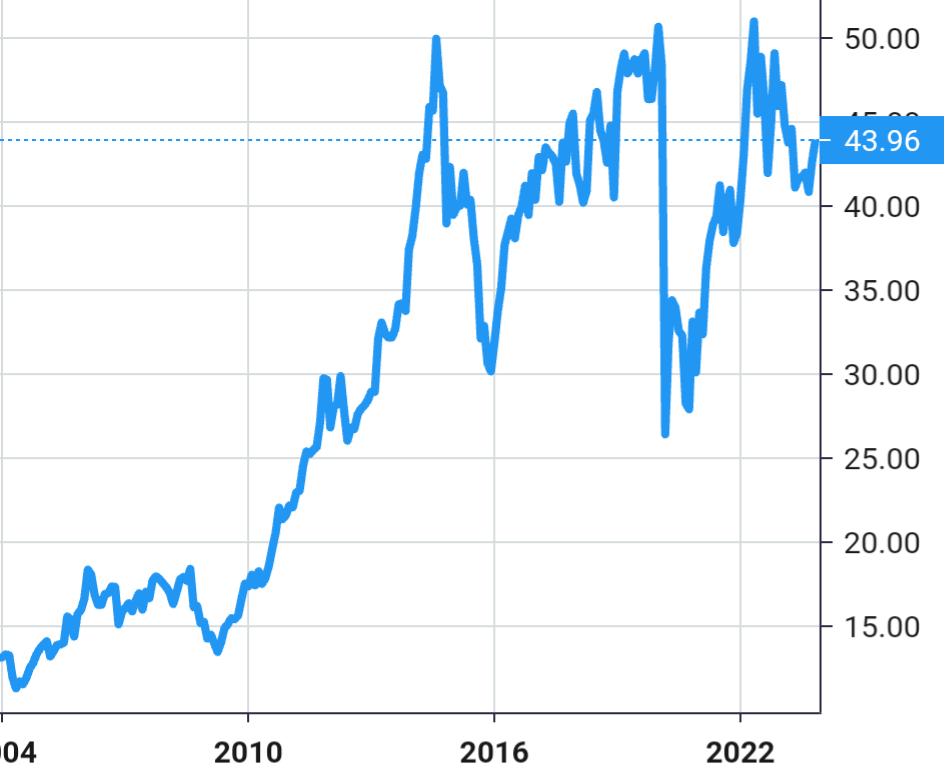
 Stock Value
Stock Value